Changes in legislation
The Order of the Federal Tax Service of the RF (FTS RF) as of 25.05.2021 No. ED-7-23/518@ approved the requirements to internal control system of the companies, in respect of which the tax monitoring is performed. We reported about the improvement of the tax monitoring system in the article as of 08.02.2021.
The new requirements were developed in order to bring the legal acts of the FTS RF into the line with the provisions of the article 14.7 of the part one of the Tax Code of the RF and the Federal Law as of 29.12.2020 No. 470-FL.
The companies should follow the requirements to the internal control system of accounting events, accuracy of calculation and retention, completeness and timeliness of payment of taxes, charges and insurance contributions, while performing the tax monitoring.
Working of the internal control system should be guaranteed on all the levels of the control of business processes performing, such as:
- before actual start of operations – in order to prevent and minimize the negative influence of events and factors, effecting on the achievement of the company’s objectives;
- during execution of operations – in order to quickly detect and eliminate violations and problems, emerging in the course of works;
- after execution of operations – in order to identify reliability of the reporting data and evaluation of the results conformity to the target or plan indicators;
As a part of the internal control system, the following options should be organized:
- control environment – standards and regulations of employment, motivation, review, career development, termination of employees, as well as requirements to the professional skills and expertise of employees;
- risk management system – a sequence of operations on prevention and minimization of the possible damage, including: risk identification, its analysis and assessment, delimitation of acceptance boundaries of risks, disclosure of information on the identified risks, making decisions on the method of risk management, based on assessing the adequacy of control procedures at the disposal of the company to cover risks;
- risk identification procedure – identification of events, situations, circumstances, making an impact on achievement of objectives of the company and analysis of the reasons and sources of the risks formation;
- assessment of the nature of the risk, based on such factors as:
association of risk with the macroeconomic changes, the changes of the social and economic situation,
association of risk with the requirements to the maintenance of accounting and tax records and preparation of reports,
complexity of the carrying out economic operations, including the necessity to perform complicated calculations and comply with the accounting principles,
degree of manual intervention into accounting process of economic operation,
degree of subjectivity in the calculation of estimated figures, contained in accounting, financial, tax and other statements,
association of risk with unethical practices; - disclosure of information on risks with description of sources of formation and criteria of risks, measures to prevent or minimize risk.
As a part of information cooperation, the taxpayers should present to the appropriate tax authorities the data on risks in electronic form; control procedures, focused on prevention and minimizations of risks; results of performing the control procedures; evaluation of the internal control system organization level; events on improvement of the internal control system; organization of the internal control system.
Moreover, the companies should perform the evaluation of the necessity to make amendments to the internal control system not less than once a quarter and present the actual data on the internal control system to the tax authorities no later than 5 working days from the date of making the amendments.
The Order will come into force since July 1st, 2021.
The information, disclosed to the tax authorities, should be presented for the reporting periods, coming up after January 1st, 2022.
Grey economy falls down
In 2020 – 2021, the volume of shady money transactions has been significantly reduced. In 2020, there was recorded a 26% decrease in such kind of transactions in the banking sector.
Cash-out transactions and withdrawal of foreign currency overseas account for the largest part of shadow schemes.
Cash-out transactions
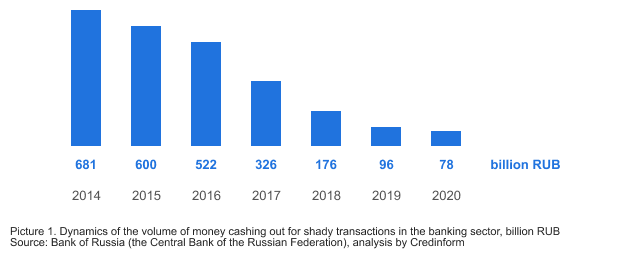
In 2020, the amount of shady transactions for money cashing out amounted to 78 billion RUB, including the issuance of funds to individuals - 59 billion RUB, to legal entities - 16 billion RUB and individual entrepreneurs - 3 billion RUB.
Over the history of the Bank of Russia keeping statistics since 2014, the volume of cash withdrawal in the banking sector has decreased 9 times (see Picture 1).
Withdrawal of funds overseas
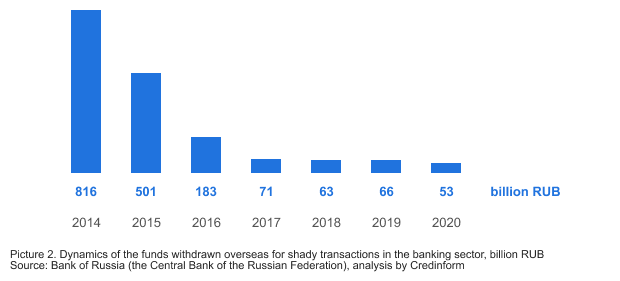
In 2020, the volume of funds withdrawn overseas under the shady schemes amounted to 53 billion RUB. In the structure of such transactions, the majority or 24 billion RUB (45%) comes from advance payments for imported goods. In addition, funds are withdrawn through payment for the import of goods from the countries of the customs union - 10 billion RUB; transfers under transactions with services - 10 billion RUB, transfers under transactions with securities - 4 billion RUB, transfers under other schemes - 5 billion RUB.
From 2014 to 2020, the volume of funds withdrawn overseas as shady transactions decreased 15 times (see Picture 2).
Sectors of economy with the highest volume of shady money transactions
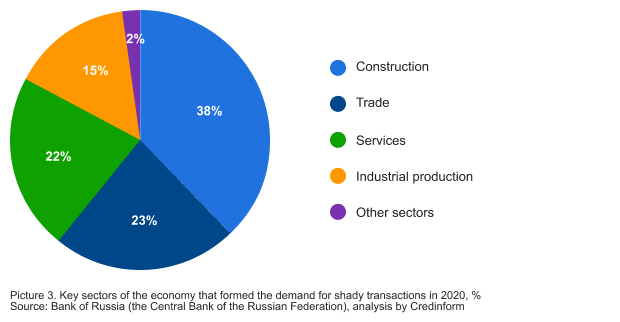
The main demand for shady financial services is coming from the construction sector - 38%, trade - 23% and the service sector - 22% (see Picture 3).
The fight against shady money transactions is taken to a new level
Since 2014, the total volume of shady money transactions for cashing out funds and withdrawing foreign currency overseas has decreased 11 times: from 1,497 billion RUB in 2014 to 131 billion RUB in 2020.
In 2020, the Bank of Russia detected and minimized the withdrawal of funds overseas through international transport channels, advertising services, and securities turnover. The volume of withdrawal of funds on multiple assignments of debt between participants in foreign economic activity has decreased.
Despite the success of the fight against the already known schemes, new illegal methods appear. In particular, signs of illegal cashing out of funds using writs of execution for fictitious debts were detected. Especially often notaries are involved, whose orders on the compulsory recovery of funds from the debtor allow to bypass court procedures. In 2020, the volume of cashing out funds under this scheme increased by more than 60% compared to 2019, and reached 25 billion RUB.
In the second half of 2021, the Central Bank of the Russia plans to launch “Know Your Client” platform for banks - a system for providing information on the level of risk of potential and existing customers being involved in shady transactions. The verification will reduce the costs of banks, as well as the number of unreasonable refusals to open and maintain accounts.
| Avoiding suspicions of shady transactions, fines and other consequences is possible only by complying with currency control legislation and AML / CFT (Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism) requirements under the 115-FL. A significant part of the work on AML / CFT within the framework of the corporate checking regulations is performed by the new Globas tool - Reports. Reports tool will help identify the company, check it against the special lists of the Federal Service for Financial Monitoring (Rosfinmonitoring) and the Federal Tax Service, identify beneficial owners, conflicts of interest, affiliation, find facts of violation of the law, and much more. |