Credit Information Regulations in Russia: who has the right to see a credit history?
Russian citizens, as well as companies residing in the Russian Federation have the right to view their own credit history. However if somebody wants to review credit history of a third person (company or consumer), prior consent is required in writing authorizing access to their credit records.
The Term “credit history” has only appeared in Russia since 2005. Since that time full information on borrowers has been collected. Credit history contains all information related to a loan: violation of terms, acceleration and full credit repayment.
A credit history contains the following parts:
"Title part of a credit history" – provides basic data on the borrower (company or consumer) including identifiers (consumer: full name, place & date of birth, pass number, Tax number, state pension fund ID number; company: company name, visiting address, Tax number, OGRN number);
"Basic part of a credit history" – provides advanced details of borrower (company or consumer) and data on payment obligations (loan amount, due date, terms of bank interest repayment etc.);
"Extra (confidential) part of a credit history" – provides creditor data and information about companies requested the credit history of a consumer or a company.
"Informational part of credit history" (on consumers only) – provides details of loan types, ways they were taken and reasons for rejecting the application.
The most relevant features in legislation that came into effect last year:
The Consumer Credit Law and the concomitant Law No.363 of Russia came into effect on July 1, 2014 amended different legal acts including the Credit History Law. One of the most important innovations: credit histories are generated now automatically, no consent of borrowers (consumers and companies) is needed. According to the former provisions of the law, a consumer or a company had to provide consent to forward and store their personal credit data in the credit reporting bureau. Since July 1st, 2014 this rule was abolished. Thus the Russian credit history legislation is being brought into line with international standards.
In addition to financial institutions since July 2014 credit history reports may be requested by employers, landlords, debt collectors and other entities and organizations provided that consent has been given by the borrower (data subject). This applies to consumers and companies.
According to the Credit History Federal Law of December 30th, 2004 No. 218-FZ, a credit reporting bureau is authorized to provide a credit history report to:
- a consumer or company acting as a borrower, according to loan agreement and in regard to which/whom this credit history is generated. A data subject may receive once a year its own credit history report free of charge;
- a company that received borrower’s (company or consumer) consent in written or electronic form to receive and view the credit history report;
- the Central catalogue of credit histories (maintained by the Central Bank of Russia): title parts of credit histories are forwarded there from all credit reporting bureaus registered in Russia;
- a court (judge) in frameworks of criminal proceeding or to a pretrial investigation body if investigation body administrator’s consent is available - extra (confidential) part of credit history;
- a federal executive body authorized to ensure proper court handling and enforcement of court decisions as well as acts issued by other authorities - title and basic parts of credit history.
A consumer is authorized to view her/his own credit history only!
Distribution, transfer, sale of any credit history data to third parties without consent of borrowers (consumers and companies) are declared illegal and lead to administrative penalty (unless such operations are part of punishable criminal offence).
Solvency ratio of automobile factories
Information agency Credinform offers to get acquainted with the ranking of Russian automobile factories. The companies with the highest volume of revenue involved in this activity were selected by the experts according to the data from the Statistical Register for the latest available period (for the year 2013). Then, the enterprises were ranked by decrease in solvency ratio.
Solvency ratio is calculated as the relation of own capital to the balance sum and shows company’s dependence on external borrowings. Recommended value of this ratio is above 0,5. The ratio is interested first of all for investors involved in long-term investing, because it characterizes company’s ability to pay off its long-term liabilities.
However, it is worth mentioning that recommended values can differ essentially as well for enterprises of different branches, as for organizations of the same industry. For getting of the most comprehensive and fair picture of the financial standing of an enterprise it is necessary to pay attention not only to industry-average indicators in the branch, but also to all presented combination of financial data.
| № | Name, INN | Region | Turnover for 2013, in mln RUB | Solvency ratio, (х) | Solvency index GLOBAS-i® |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Rus LLC INN 7801463902 |
Saint-Petersburg | 79 754 | 0,53 | 179 (the highest) |
| 2 | Kamaz OJSC INN 1650032058 |
Republic of Tatarstan | 107 221 | 0,52 | 174 (the highest) |
| 3 | Renault Russia CJSC INN 7709259743 |
Moscow | 105 949 | 0,48 | 179 (the highest) |
| 4 | Nissan Manufacturing Rus LLC INN 7842337791 |
Saint-Petersburg | 124 834 | 0,3 | 253 (high) |
| 5 | Volkswagen Group Rus LLC INN 5042059767 |
Kaluga region | 241 249 | 0,28 | 217 (high) |
| 6 | Ford Sollers Holding LLC INN 1646021952 |
Republic of Tatarstan | 84 047 | 0,23 | 311 (satisfactory) |
| 7 | Avtovaz OJSC INN 6320002223 |
Samara region | 175 152 | 0,17 | 285 (high) |
| 8 | Avtomobilny Zavod Gaz LLC INN 5250018433 |
Nizhnii Novrorod region | 68 839 | 0,11 | 244 (high) |
| 9 | Avtotor CJSC INN 3905011678 |
Kaliningrad region | 42 839 | 0,08 | 222 (high) |
| 10 | Ellada Intertreid LLC INN 3906072056 |
Kaliningrad region | 79 129 | 0,02 | 249 (high) |
The previuos year turned out to be a mixed year for the Russian car market. On the one hand, in December 2014 it was sold a record number of cars in the history of domestic car market – 270,7 ths automobiles and LCVs, that is by 2,4% more than for the similar period of 2013. Excessive demand in December of the previuos year was caused by devaluation of the rouble and fall in oil prices. However, in spite of automobile boom in December, the Russian car market declined by 10,3% at year-end 2014. The experts forecast even more substantial contraction of the market in the current year due to the decline in demand and increase in the cost of automobiles. The companies, depending on the import of vehicles and constituent parts, are at risk.
The first three leaders of the ranking are as follows: Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Rus LLC (solvency ratio value is 0,53), Kamaz OJSC (0,52) and Renault Russia CJSC (0,48). The values of solvency ratio of these enterprises meet generally accepted requirements or are a little behind. In support of good results all companies got the highest solvency index GLOBAS-i®, that points to the ability of the enterprises to pay off their debts in time and fully.
The company Ford Sollers Holding LLC, the only one from the TOP-10 list, got a satisfactory solvency index GLOBAS-i®, that testifies to the solvency level, which doesn’t guarantee that debts will be paid off in time and fully. At year-end 2013 the cumulative turnover of the enterprise reduced by 10%.
The rest enterprises of the ranking, in spite of low values of the solvency ratio, got a high solvency index GLOBAS-i®, considering the combination of financial and non-financial indicators.
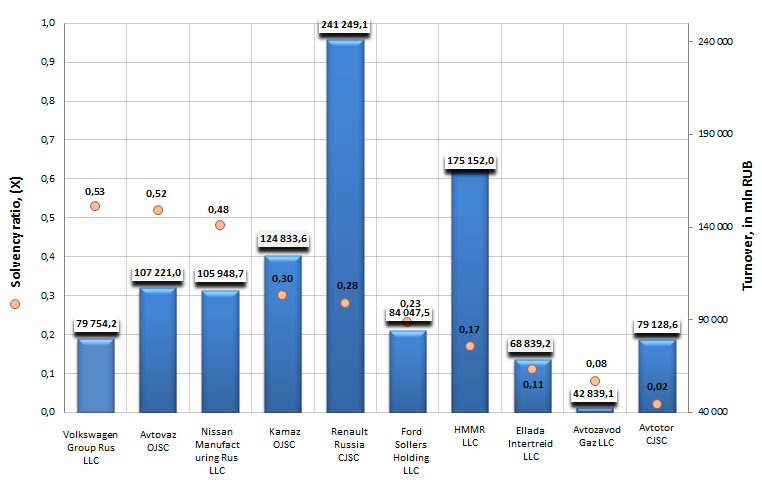
Solvency ratio of automobile factories in Russia, TOP-10
Contraction of the market forced a number of major players to announce the suspension of production. In spring of the current year General Motors Auto LLC announced the suspension of production for almost two months. Avtovaz OJSC announced the reduction of about 1100 executives of different levels. And it’s far from a complete list of messages about negative trends in automobile industry. Thus, some companies prepaire to the decline in capacities.
Decline in demand and complicated situation on the market forced Russian car manufacturers (including foreign concerns) to apply to the government with request to take a set of measures to encourage Russian car market. However, their offers were accepted only to a limited volume.
The government agreed to prolong the scrappage program, on which 10 bln RUB were allocated with the possibility of limit increase. Moreover, the branch will be supported by public procurements and subsidies for purchase of agricultural, municipal and other socially minded machines.
Along with that, many measures focused on the support of light car industry were rejected. Thus, the govermnment didn’t support the idea of resuming of the program of soft automotive lending, for which the union of car dealers asked 20 bln RUB.
At the same time, the economic situation can spur manufacturers to develop and localize their production on the territory of Russia. Thus, the plant Nissan Manufacturing Rus LLC, near St.-Petersburg, plans to increase the localization from 39% up to 45% in the near future.
However, the process of localization holds also hidden dangers. The transfer of production capacities not always leads to costs reduction in roubles equivalent, because, as a rule, constituent parts used by assembly are imported. In addition, it needs time to implement the plan of localization of production even in urgent term.
See also: Solvency ratio of enterprises involved in advertising business