Dynamics of investment activity in Russia: state and prospects
In 2014 there was a slump of foreign investment in the Russian economy. According to the data of the Bank of Russia, direct foreign investment in the non-banking sector of RF were amounted to USD 20, 2 bln., following the results of the first half of 2014; that is 52% less than in the same period of 2013.
Sanctions from the Occident as well as economic slowdown and devaluation of the rouble have resulted in reduction of the foreign capital inflows. A high degree of uncertainty concerning the country’s economy development still remains; that makes investors to wait for better period. At the same time active investment inflow in 2018 is expected due to the gas supply through the Sila Sibiri (the Power of Siberia) gas pipeline and holding FIFA World cup in Russia.
One of the sources of investment in the economy of RF can be foreign legal entities, acting as shareholders of Russian companies. According to the data of the Information and analytical System GLOBAS-i of Credinform agency, 47 954 companies with foreign shareholders are registered in Russia. 53% of them own 100% of authorized capital. It bears reminding, that in 2013 this index was 52%.
The majority of 47 954 companies with foreign capital are located in Moscow and Moscow region (62,3%), Saint-Petersburg and Leningrad region (10,8%) and the Krasnodar Territory (2%). Companies with the following activity types are leaders among Russian enterprises: wholesale, lease of own real estate and consulting in the field of business and management.
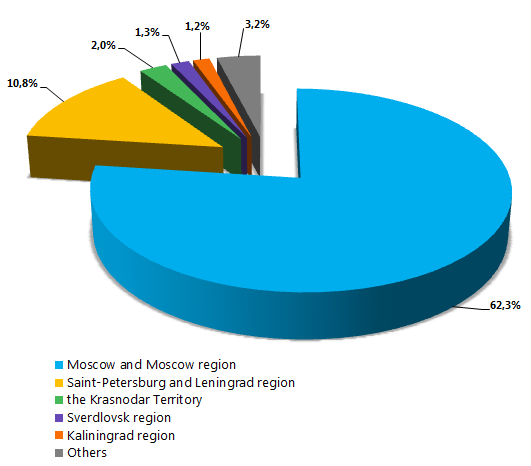
Figure. Allocation of companies with foreign capital by the subjects of Russia
Slump of foreign investment in the Russian economy is observed against capital outflow. According to the data of the Higher School of Economics, net capital outflow from Russia has exceeded USD 110 bln from January 2014; that goes beyond all official forecasts. As a reminder, in the estimation of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation net capital outflow for 2014 had to be amounted to USD 100 bln. At the same time the Bank of Russia has announced USD 90 bln amount.
However devaluation of the rouble together with food embargo have resulted in total imports reduction; this helped to strengthen the trade balance under the conditions of export revenue stagnation. As a result monies transferred in Russia not only exceeded payments to other countries and international organizations, but also doubled for 3 quarters of 2014 and amounted to USD 52,3 bln in comparison with the same period of the previous year. Almost two-thirds of its growth is accounted for reduction of visible imports by 6,4%, to the amount of USD 232,7 bln. At the same time export remains at last year’s level with amount of USD 383,8 bln.
Foreign investment play a major role in the development of the country’s economy, because modern technologies, new management methods, highly qualified specialists are attracted together with investment; manpower skills also grows.
Along with that the general trend of capital outflow from emerging markets should be noted. Investors are waiting for stabilization of the situation with the object of getting high return on investment. But in spite of even the most favorable rates, the situation can be stabilized not earlier than in the second half of 2015.
The upcoming 2015 will be a year of challenges and difficult decisions
The year of 2014, which was rich in events and has set new challenges for the country, is drawing to a close. Russia has entered an unfavorable stage of the economic cycle, which will be influenced in the medium term by economic sanctions, falling of oil prices, devaluation and acceleration of inflation.
Negative processes in the economy have resulted in a perceptible slowdown in the consumption growth of the population, proving by the reduction in retail trade turnover from 3.6% in I quarter to 1.8% in the II quarter this year. A raise of key rate by Central Bank to 9.5% in the future can significantly chill the activity in the domestic borrowing market. Tense geopolitical situation makes the leading investors nervous. Currently serious infrastructure solutions are required from the state, which is now more relevant than ever.
All this affects the key macroeconomic indicators - GDP growth, which is slowing down for three consecutive quarters and absolutely does not correspond to the potential capabilities and needs of the country for the development of existing and new industries, creating jobs in the service sector.
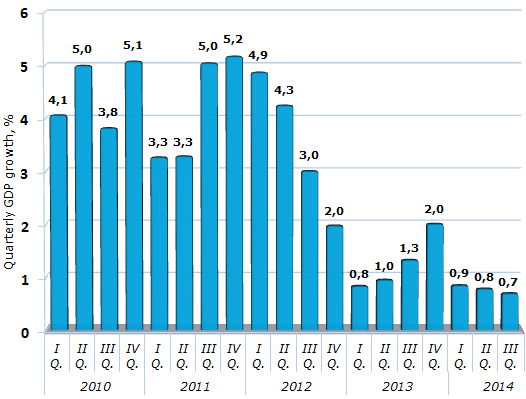
Figure 1. Quarterly GDP growth rate of the corresponding period of the previous year,%
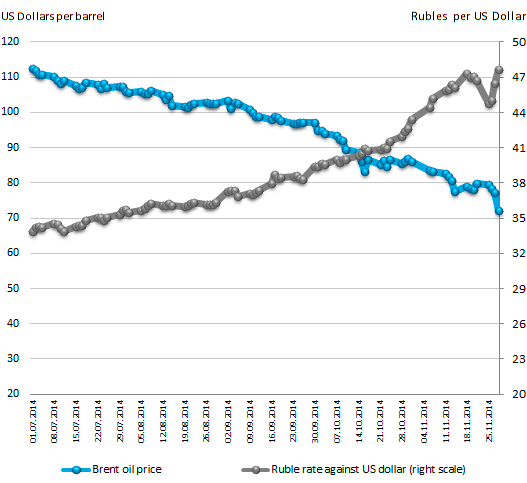
Figure 2. Dynamics of prices for Brent oil and the Russian ruble against the US dollar
Against the background of the rapid devaluation of the national currency, the historic decision of the Bank of Russia to cancel the currency basket corridor and regular foreign exchange intervention from November 10, 2014 has gone almost unnoticed. Floating exchange rate determined by market forces - is an important step towards full convertibility of the ruble, means of international payments and reserves.
The falling ruble is under enormous pressure of market participants due to lower of oil prices.
On the one hand, a weak ruble compensates losses of the budget from foregone export revenues; on the other hand – companies, attracting loans in the foreign market, will feel the sting of extra costs for loans service increased in price. Large list of products purchased abroad also increased in price. All this will lead to the acceleration of inflation and the deterioration of the growth dynamics of the population’s real wages and pensions.
However, despite the current geopolitical turbulence, a healthy optimism should be kept. The upcoming 2015 will be a year of challenges and difficult decisions that finally define new growth points and ways to diversify the economy.