Receivables turnover of printing companies and publishing houses in Russia
Information agency Credinform prepared a ranking of receivables turnover of printing companies and publishing houses in Russia. The ranking list includes 10 largest Russian companies with this activity and is based on turnover as stated in the Statistics register, with the reference period of 2011. These companies were ranked first in terms of revenue, and then of ascending the receivables turnover ratio.
Receivables turnover indicates the number of days required to recover the debt. The lower the number, the faster the receivables turn into cash and, therefore, increase the liquidity of working capital. For an objective assessment of the indicator, it should be analyzed alongside the payables turnover ratio: number of days of payables turnover should exceed the number of days of receivables turnover.
| № | Name, INN | Region | Turnover 2011, mln. RUB | Receivables turnover, days | Solvency index GLOBAS-i® |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Print House Pushkinskay Ploshad, INN 7723193075 | Moscow | 2 937 | 13,72 | 332 (satisfactory) |
| 2 | JSC "Publishing House "Rossiyskaya gazeta", INN 7714010896 | Moscow | 3 858 | 13,83 | 193 (top) |
| 3 | LLC First printing and publishing plant, INN 5024051807 | Moscow region | 2 737 | 22,45 | 338 (satisfactory) |
| 4 | LLC Fashion Press, INN 7743002018 | Moscow | 2 945 | 69,58 | 195 (top) |
| 5 | CJSC "Conde Nast", INN 7709244433 | Moscow | 2 366 | 69,82 | 164 (top) |
| 6 | JSC "Prosveshcheniye publishers", INN 7715589549 | Moscow | 3 701 | 84,15 | 206 (high) |
| 7 | CJSC "Kommersant. Publishing House", INN 7707120552 | Moscow | 2 488 | 102,19 | 226 (high) |
| 8 | "Hearst Shkulev Media" LLC, INN 7708183322 | Moscow | 2 417 | 105,01 | 220 (high) |
| 9 | Publishing house "Komsomolskaya pravda", INN 7714037217 | Moscow | 4 903 | 105,86 | 206 (high) |
| 10 | Eksmo Publishing House LLC, INN 7708188426 | Moscow | 4 651 | 166,96 | 197 (top) |
Today the publishing industry worldwide is in decline in all indicators and the Russian market is no exception. Many experts explain negative tendencies with sales slowdown for printed literature because of the demographic crisis accompanied by differentiation of reader demand and the increasing popularity of electronic media and Internet resources.
In the domestic publishing market the leading positions belong to Moscow companies. In the ranking top-10 includes nine Moscow companies and one company of the Moscow region.
The ranking top-3 is as follows: Print House Pushkinskay Ploshad, JSC "Publishing House "Rossiyskaya gazeta" and LLC First printing and publishing plant. Receivables turnover of these companies does not exceed 23 days. It should be noted that according to an independent evaluation of the creditworthiness of the Information agency Credinform, only JSC "Publishing House "Rossiyskaya gazeta" was given the highest solvency index GLOBAS-i ®, which describes the company as a financially stable. Two other companies were given a satisfactory solvency index GLOBAS-i ®, which means that firms do not guarantee the full and timely repayment of its debt obligations.
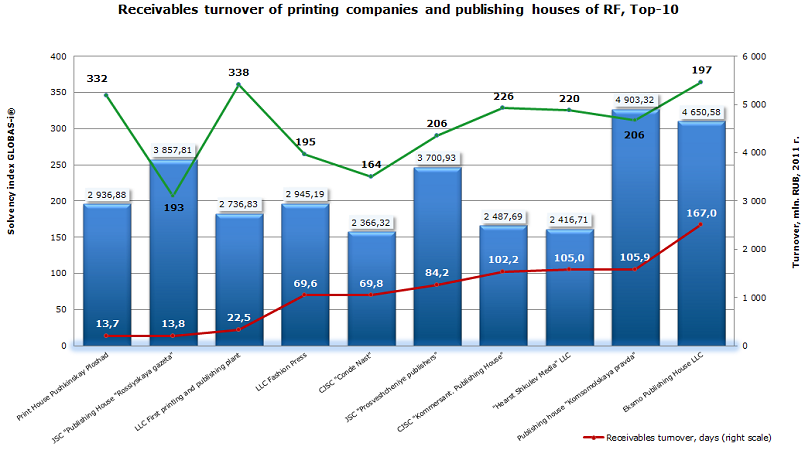
The undisputed leader of the Russian printing market is Eksmo Publishing House LLC, both in terms of circulation and titles released, closes the top-10 of largest producers, with the highest rate of receivables turnover - 167 days. Despite this, the company has been assigned the highest solvency index GLOBAS-i ®. Another major typographic venture, JSC "Prosveshcheniye publishers" settled only on the sixth line of the ranking, having a high solvency index GLOBAS-i ®.
Based on these ranking results it is possible to ascertain the necessity to take into account the collection of financial indicators for an objective assessment of the company’s solvency and financial stability.
G-20 Saint Petersburg Summit: the results and directions balanced development of the world economy
Last week in St. Petersburg (the first time in Russia) the G-20 (a group of the largest economies in the world (industrial Twenties)) Summit has been closed.
In the course of the summit, member countries have pledged to implement a series of reforms to create the conditions for sustainable and balanced growth in the long term. This will be achieved by working in the following areas:
1. Unemployment and underemployment, particularly among young people, are among the main challenges of the global economy. It is necessary to improve the business climate and stimulate the creation of more productive and well-paid jobs; to invest the development of the skills, quality education programs and continuing education throughout a person's life; to stimulate the target financing in the infrastructure of the labor market, to improve the quality of jobs and working conditions.
2. Attracting investment. Countries have admitted the key role of long-term investment in sustained global economic growth ensuring. Therefore it was planned to develop a comprehensive approach to identify and remove obstacles to the mobilization of private capital and improve investment conditions and the efficiency of state investment.
3. Improving global trade. World leaders have pledged to take the responsibility to fight against protectionism as the main obstacle to a transparent and competitive trade, including through more effective use of existing WTO rules.
4. The fight against tax evasion. The heads of states have come to a consensus on the issue of taxation of profit: profit should be taxed where entrepreneurial activity is conducted, where value is created. That directly concerned G-20 countries, which account for most of the world's GDP.
5. The international financial architecture. During previous summits it was agreed to increase the value of the IMF in the prevention and resolution of crises and maintaining global financial stability by increasing temporary financial resources available to the IMF. In St. Petersburg, the meeting participants concluded that today accounts FIP accumulated more than USD 461 billion. These resources are aimed at providing assistance to low-income countries in the development of conservative medium-term debt management strategies and increase their capacity to debt management.
6. Financial regulation. G-20 agreed on the implementation of the financial regulation reforms to reduce the risk of misconduct and systemic risks. The work on the convergence of financial reporting standards in order to increase the stability of the financial system, meeting the standards in the field of international cooperation and information exchange for financial supervision and regulation, reduction of risks associated with the operation of the shadow banking system, resolve issues of money laundering and terrorist financing is continuing.
7. Sustainable energy policy. Issues relating to the introduction of the green economy, clean energy technologies and energy security for long-term prosperity and well-being of present and future generations were discussed in the course of the summit.
8. Strengthening the fight against corruption. The fight against corruption by increasing transparency and improving measures to real observance of anti-corruption rules and obligations, including through the ratification of the UN Convention against Corruption was also discussed. By the way, Russia has not yet ratified the Article 20 of the Convention, implying a fight against the illicit enrichment of public officials.
In addition to the world's economic problems, the summit participants paid attention to the war in Syria. In this matter reaching an agreement has failed. Eleven countries have declared their support for U.S. action on military intervention in Syria, even in the absence of the mandate of the UN Security Council. Russia, the hostess of the meeting, opposes such military intervention. Open warfare could only tighten the knot of the conflict, and the consequences will incalculably affect the fragile world economy.