New data in The Tax Service to check counterparties
On August 1, 2019, the Federal Tax Service of Russia (FTS) disclosed information on average number of employees, applying special tax regimes by companies, and inclusion in consolidated group of taxpayers for 2018.
1 or 0 employee is the average number of stuff in 56% of companies in Russia.
Data on the average number of employees for 2018 is disclosed for 2,4 million legal entities (out of 4,1 million legal entities on December 2018). Detailed data structure is presented on Picture 1.
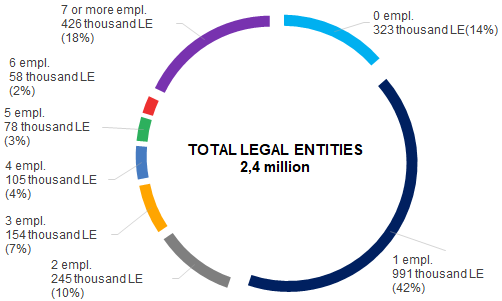 Picture 1. Average number of employees according to the FTS on December 31, 2018
Picture 1. Average number of employees according to the FTS on December 31, 2018The companies are obliged to submit data of the average number of stuff to the FTS, even if there are no regular employees.
One of the reasons there are companies with small and zero number of employees is that part-timers and contractors are not included in the number of stuff. The other reason is tax optimization. The labor compensation fund is obliged to pay social due that is why the employers do not take on stuff.
At counterparties check, the number of stuff is necessary to be taken into account. Companies with 0 or 1 employee are at the risk, because small or zero number of employees is one of the negative signs.
Excluding statistical companies, major taxpayers and enterprises of defense industry, data on which will be disclosed on 2020, the largest Russian company in term of the number of stuff in 2018 is JSC Svyaznoy Logistics with 16 276 employees. The company is dissolved due to the reorganization in the form of acquisition by LLC Svyaznoy Chain (see Table 1).
Table 1. Top-10 of the Russian companies by the average number of employees
| Rank | Company | Average number of employees in 2018 | Revenue in 2018, million RUB |
| 1 | JSC SVYAZNOY LOGISTICS | 16 276 | 109 862 |
| 2 | LLC GAZSTROY | 16 112 | 36 146 |
| 3 | LLC SIBERIAN INTERNET COMPANY | 15 334 | 49 298 |
| 4 | JSC ILIM GROUP | 14 963 | 155 701 |
| 5 | JSC ER-TELECOM HOLDING | 14 737 | 34 979 |
| 6 | LLC ELDORADO | 13 620 | *110 406 |
| 7 | LLC SELTA (Magnit Group) | 13 007 | 38 531 |
| 8 | LLC RUSSIAN ENGINEERING COMPANY | 12 680 | 32 870 |
| 9 | LLC UNITED SERVICE COMPANY | 12 609 | 12 749 |
| 10 | JSC MEGAFON RETAIL | 11 360 | 41 035 |
(*) data on 2017
Simplified tax system (STS) is the most spread tax regime in Russia.
According to the FTS, 89% or 1,4 million out of 1,6 million companies having applied one or several special tax regimes, use simplified tax system (Picture 2). 5% of legal entities combine STS and imputed income of individual entrepreneurs (UTII). Special tax regime allows companies to pay one general tax at reduced rate instead of income tax, property tax and VAT.
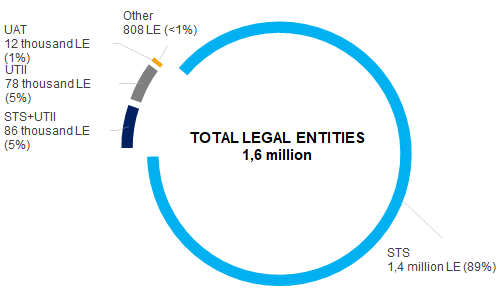 Picture 2. Distribution of companies by applied special tax regimes in 2018
Picture 2. Distribution of companies by applied special tax regimes in 2018Criteria of applying special tax regimes help to have an overall characteristics of business at the counterparty analysis: to assess total income, net assets value, number of employees, field of activity.
The fact of applying the STS by the counterparty is indicative of income not exceeding 150 million RUB per year, the number of stuff is up to 100 employees, the cost of fixed assets is less than 150 million RUB, the counterparty does not belong to organizations activities of which are especially strictly controlled by the state (banks, insurance companies, manufacturers of excisable goods, budget institutions), does not pay income taxes, taxes on property of organizations and VAT.
Participation in the consolidated group of taxpayers is the prerogative of large business.
Consolidated group of taxpayers is a voluntary association of organizations created to pay income tax on consolidated financial result of the entire group. Responsible member of the consolidated group is assigned to calculate and pay income tax.
Consolidated group of taxpayers can be created if one company directly or indirectly participates in the authorized capital of other companies, and the share of such participation in each legal entity is at least 90%.
According to the data for 2018, the FTS published information on 210 responsible members of the consolidated group. In 2017, there were 88 such participants.
While checking business partners or counterparties, their participation in consolidated group of taxpayers is indicative of belonging to a vertically integrated holding headed by major taxpayers, taxation and business of which are strictly controlled and extremely transparent.
Data, publication of which on the FTS resource is expected by the year-end, will also be placed in Globas:
On October 1, 2019, the FTS plans to publish information on income and expenses from the financial statements of organizations, as well as information on taxes, fees and insurance contributions paid in 2018.
On December 1, 2019, the FTS is expected to disclose information on arrears, tax debts, arrears of insurance premiums, and information on tax violations.
Settlement arrangements in arbitration
New settlement arrangements were set within the legal proceedings in general jurisdiction and arbitration courts.
Relevant changes were made to the Code of Administrative Judicial Procedure, Arbitral Procedural Code and Civil Procedural Code of the Russian Federation by the Federal Law of July 26, 2019 №197-FL.
It is worth reminding that among settlement arrangements are negotiations, intermediation, including mediation, judicial conciliation and other arrangements, which do not contradict the legislation of Russia.
The changes fixed the following:
- the procedure and terms of implementation of settlement arrangements;
- requirements to the form and content of the settlement agreement, procedures for its approval by the court and execution were defined;
- retired judges got the right to be a mediator or judicial conciliator;
- the procedure for notary certification of mediation agreements reached by the parties in accordance with the mediation procedures provided by the Federal law «On alternative dispute resolution procedures involving an intermediary (mediation procedure)» were defined;
- mediation agreements or their notarized copies are referred to the execution orders, which should be sent to court bailiff.
The changes will come into force on October 25, 2019 except separate provisions, which will come into force on other dates.