Legislation amendments
In 2021, a new Regulation on licensing of activities related to the handling of industrial explosives will come into force. This is approved by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 15, 2020 No. 1435.
The licensing authority is the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological, and Nuclear Supervision (Rostekhnadzor).
Among the licensed activities are production, storage and use of industrial explosives.
The license applicants must meet the following requirements:
- availability of own relevant non-residential premises, buildings, structures and other objects or objects owned on other legal grounds;
- availability of own necessary technical devices and test and control equipment or equipment owned on other legal grounds, as well as technical documentation;
- availability of permanent staff member with the authority to make organizational decisions on implementation of the claimed work, with higher or secondary professional (technical) education, work experience in this field for at least 1 year, who meets the qualification requirements for the claimed work and is certified in accordance with the requirements of the Federal law "On industrial safety of hazardous production facilities»;
- keeping the records of industrial explosive materials in accordance with standards and regulations in the field of industrial safety;
- compliance of applied technical devices with mandatory requirements of technical regulations;
- technical devices must have positive expert reports on industrial safety entered in the relevant register;
- industrial safety management and production control systems organization.
The state fee is imposed on the granting and renewal of licenses.
The Regulation will come into force on January 1, 2021 and will be valid until January 1, 2027.
All information related to the entities involved in production, storage and use of industrial explosives (including historical data) is available in the Information and Analytical system Globas. Currently, more than 1400 companies have licenses for these types of activities.
Economy in Samara in crisis years
The impacts of the previous 2008 - 2009 global financial crisis were overcome only by 2011. By that moment more than 26 thousand companies had been operating in Samara.
Information agency Credinform represents a review of the activity trends of the largest companies of the real economy in Samara during the financial crisis of 2008 – 2009 years.
ДThe largest enterprises in Samara (TOP-1000) in terms of annual revenue were selected for the analysis according to the data from the Statistical Register for the period of 2006 – 2011 years. The analysis was based on the data from the Information and Analytical system Globas.
Number of active companies
From 2006 to 2011, the number of active companies increased, but the growth rates decreased especially during the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery.
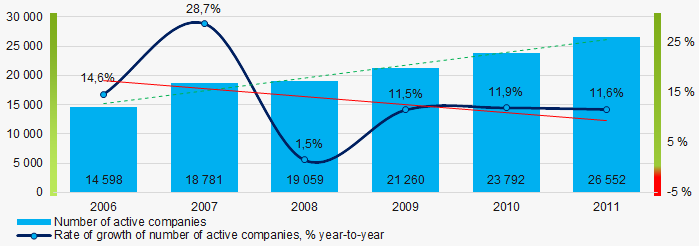 Picture 1. Change in the number of active companies in 2006 – 2011
Picture 1. Change in the number of active companies in 2006 – 2011Net assets are total assets less total liabilities. This indicator reflects the real value of the property of an enterprise. When the company’s debt exceeds the value of its property, the indicator is considered negative (insufficiency of property).
The largest company of the real sector of economy in Samara in term of net assets was AO TRANSNEFT-PRIVOLGA, INN 6317024749. In 2011, net assets value of the company amounted to more than 90 billion RUB, in 2019 – to almost 201 billion RUB.
The lowest net assets value among TOP-1000 was recorded for JSC "VOLZHSKI OIL SHIPPING COMPANY "VOLGOTANKER", INN 6317019185, in process of being wound up since 17.03.2008. In 2011, insufficiency of property of the company was indicated in negative value of -3,2 billion RUB, and in 2019 the figure amounted to -1,2 billion RUB.
In 2006 - 2011, the average net assets values of TOP-1000 had a general trend to increase, however the growth rates were decreasing especially during the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery. (Picture 2).
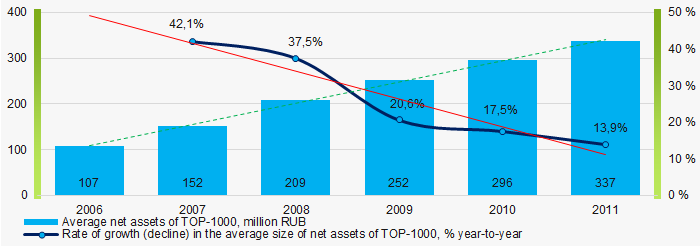 Picture 2. Change in average net assets value in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 2. Change in average net assets value in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011In general, the shares of TOP-1000 companies with insufficient property had a trend to decrease in 2006-2011(Picture 3).
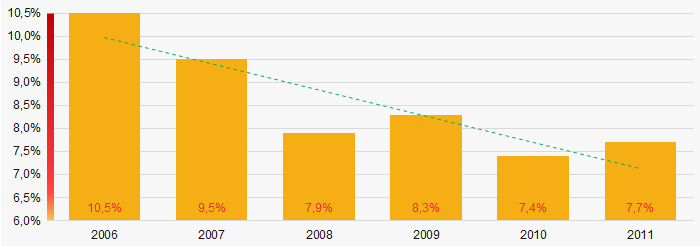 Picture 3. Shares of companies with negative net assets value in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 3. Shares of companies with negative net assets value in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011Sales revenue
The largest company of the real sector of economy in Samara by revenue was JSC SAMARANEFTEGAS, INN 6315229162. The revenue volume amounted to 99 billion RUB in 2011, and rolled over to 255 billion RUB in 2019.
In general, there was a trend to increase in revenue with decreasing growth rate during the acute phase of the crisis (Picture 4).
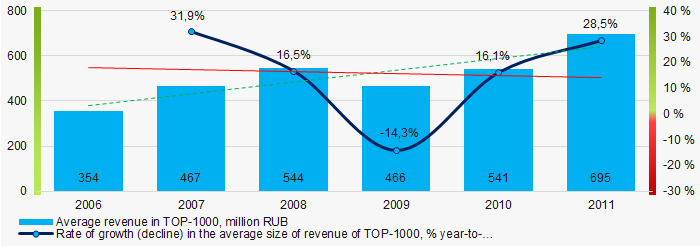 Picture 4. Change in average revenue in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 4. Change in average revenue in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011Profit and loss
The largest company of the real sector of economy in Samara in term of net profit was as well JSC SAMARANEFTEGAS, INN 6315229162. The company’s profit amounted to 30 billion RUB in 2011, and it increased to 53 billion RUB in 2019.
During the period of 2006 – 2011, the average profit figures of TOP-1000 companies had a general trend to increase with decreasing growth rate especially during the acute phase of the crisis (Picture 5).
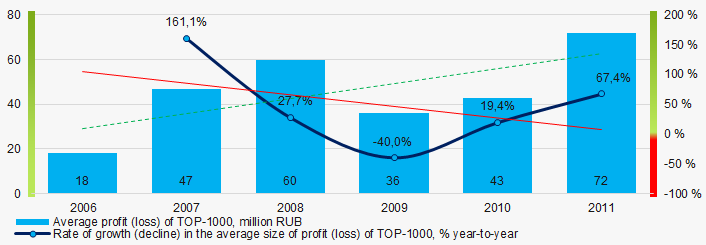 Picture 5. Change in average profit (loss) in TOP-1000 in 2006- 2011
Picture 5. Change in average profit (loss) in TOP-1000 in 2006- 2011In 2006 – 2011, the average net profit figures of TOP-1000 companies had a general trend to increase, while the average net loss decreased (Picture 6).
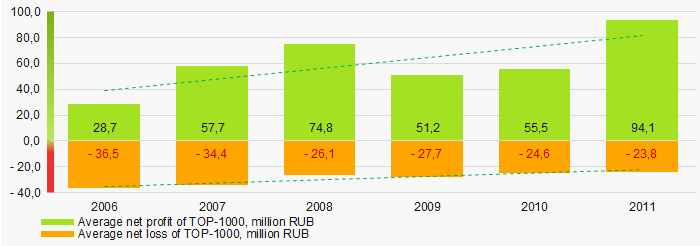 Picture 6. Change in average net profit and net loss in ТОP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 6. Change in average net profit and net loss in ТОP-1000 in 2006 – 2011Key financial ratios
In 2006 – 2011, the average values of the current liquidity ratio of TOP-1000 were above the recommended one – from 1,0 to 2,0, with a trend to increase. (Picture 7).
Current liquidity ratio (current assets to short-term liabilities) shows the sufficiency of company’s assets to repay on short-term liabilities.
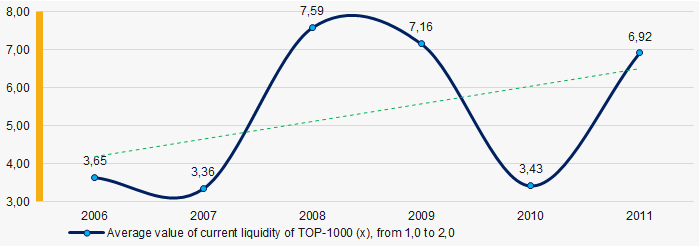 Picture 7. Change in average values of current liquidity ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 7. Change in average values of current liquidity ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011At the period of 2006 – 2011, there was a general trend to decrease in the averageROI values (Picture 8).
ROI ratio is calculated as net profit to sum of shareholders equity and long-term liabilities, and shows the return of equity involved in commercial activities and long-term borrowed funds.
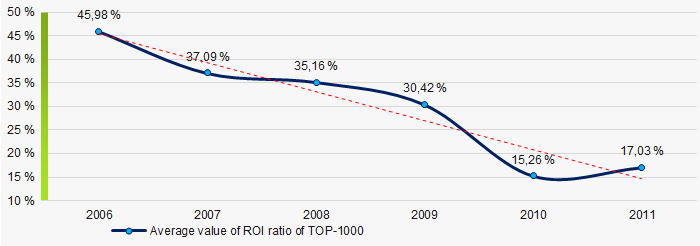 Picture 8. Change in average values of ROI ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 8. Change in average values of ROI ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011Assets turnover ratio is the ratio of sales revenue and company’s average total assets for a period. It characterizes the effectiveness of using of all available resources, regardless the source of their attraction. The ratio shows how many times per year the full cycle of production and circulation is performed, generating the corresponding effect in the form of profit.
In 2006 – 2011, there was a trend to decrease of this ratio, especially during the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery. (Picture 9).
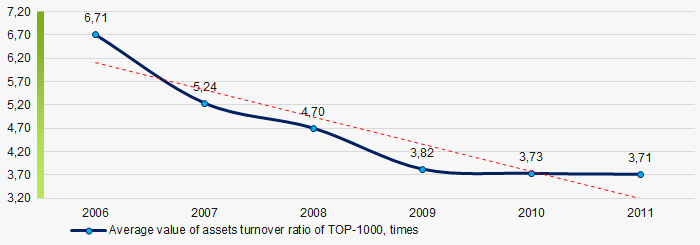 Picture 9. Change in average values of assets turnover ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011
Picture 9. Change in average values of assets turnover ratio in TOP-1000 in 2006 – 2011Small enterprises
56% companies of TOP-1000 are registered in the Register of small and medium-sized enterprises of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation. However, their share in total revenue of TOP-1000 amounted 13% in 2011 (Picture 10).
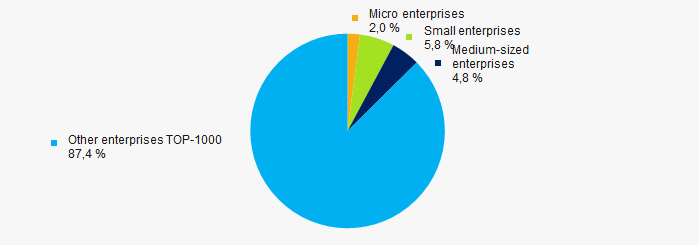 Picture 10. Shares of revenue of small and medium-sized enterprises in TOP-1000 in 2011
Picture 10. Shares of revenue of small and medium-sized enterprises in TOP-1000 in 2011Financial position score
According to the assessment, the financial position of most of TOP-1000 companies is average in 2020. At the same time, index wasn’t assigned to 1/3 enterprises, which indicates the fact that these companies doesn’t have financial accounts. (Picture 11).
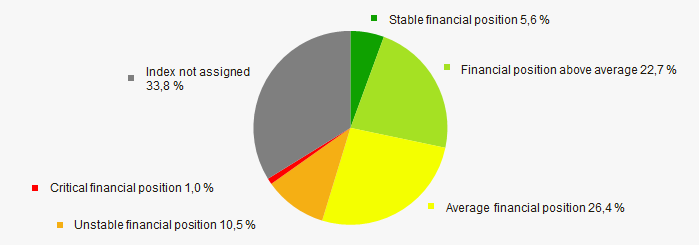 Picture 11. Distribution of TOP-1000 companies by financial position score in 2020
Picture 11. Distribution of TOP-1000 companies by financial position score in 2020Solvency index Globas
In 2020, almost the half of TOP-1000 companies got Superior / High and Strong / Medium index Globas. This fact shows their ability to meet their obligations fully and by the due date (Picture 12). However, more than one third of enterprises have Insufficient value.
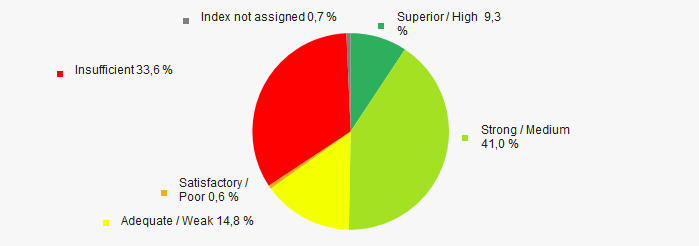 Picture 12. Distribution of TOP-1000 companies by solvency index Globas
Picture 12. Distribution of TOP-1000 companies by solvency index GlobasConclusion
Complex assessment of activity of the largest companies of the real economy sector of Samara, taking into account the main indexes, financial ratios and indicators, demonstrates the prevalence of negative trends in 2006 - 2011 (Table 1).
| Trends and evaluation factors | Relative share of factor, % | Possible forecast |
| Dynamics of the number of active companies |  10 10 |
|
| Rate of growth of the number of active companies |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, rate of growth of the number of active companies may be decreased |
| Dynamics of the average net assets value |  10 10 |
|
| Rate of growth (decline) in the average size of net assets |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, rate of growth in the net assets may be decreased |
| Increase / decrease in the share of enterprises with negative values of net assets |  10 10 |
|
| Dynamics of the average revenue |  10 10 |
|
| Rate of growth (decline) in the average size of revenue |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis, rate of growth in revenue may be decreased |
| Dynamics of the average profit |  10 10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, the average profit may be decreased |
| Rate of growth (decline) in the average size of profit |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, rate of growth in the average size of profit may be decreased |
| Growth / decline in average values of companies’ net profit |  10 10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, net profit may be increased |
| Growth / decline in average values of companies’ net loss |  10 10 |
|
| Increase / decrease in average values of current liquidity ratio |  5 5 |
|
| Increase / decrease in average values of return on investment ratio |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, return on investment ratio may by decreased |
| Increase / decrease in average values of asset turnover ratio, times |  -10 -10 |
During the acute phase of the crisis and the period of recovery, business activity may by decreased |
| Share of small and medium-sized businesses in terms of revenue being more than 20% |  -10 -10 |
|
| Financial position (the largest share) |  5 5 |
|
| Solvency index Globas (the largest share) |  5 5 |
|
| Average value of relative share of factors |  0,9 0,9 |
 positive trend (factor),
positive trend (factor),  negative trend (factor).
negative trend (factor).