Solvency ratio of public catering companies
Information agency Credinform has prepared a ranking of the largest Russian public catering companies. The largest enterprises (TOP-10) in terms of annual revenue were selected according to the data from the Statistical Register for the available periods (2006-2011). Then the companies were ranged by solvency ratio (Table 1). The analysis was based on the data from the Information and Analytical system Globas.
Solvency ratio (х) is calculated as a ratio of equity capital to total balance. The ratio shows the company’s dependence from external borrowings. The recommended value of the ratio is >0,5.
The ratio value less than minimum limit signifies about strong dependence from external sources of funds; such dependence may lead to liquidity crisis, unstable financial position in case of deterioration in market conditions.
For the most full and fair opinion about the company’s financial position the whole set of financial indicators and ratios should be taken into account.
| Name, INN, region, trademark | Revenue, million RUB | Net profit (loss), million RUB | Solvency ratio (x), >0,5 | Solvency index Globas 2020 | |||
| 2009 | 2011 | 2009 | 2011 | 2009 | 2011 | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| JSC MOSCOW-MCDONALD'S INN 7710044132 Moscow (MCDONALDS, HAPPY MEAL, BIG MAC, Quarter Pounder, Filet-O-Fish, MCHAPPY PLACE, ROYAL CHEESEBURGER, MCCAFE, Big Tasty) |
 12 190,5 12 190,5 |
 12 196,2 12 196,2 |
 890,0 890,0 |
 941,5 941,5 |
 0,86 0,86 |
 0,85 0,85 |
155 Superior |
| LLC MCDONALD'S INN 7710044140 Moscow |
 21 049,4 21 049,4 |
 34 145,0 34 145,0 |
 1 983,3 1 983,3 |
 3 679,9 3 679,9 |
 0,85 0,85 |
 0,80 0,80 |
176 High |
| LLC FASTLAND INN 7703234453 Moscow (MU-MU) |
 1 503,4 1 503,4 |
 2 415,6 2 415,6 |
 76,0 76,0 |
 160,6 160,6 |
 0,31 0,31 |
 0,65 0,65 |
239 Strong |
| JSC AEROMAR INN 7712045131 Moscow region (SKYSERVICE, AEROMAR) |
 2 801,8 2 801,8 |
 5 082,4 5 082,4 |
 307,9 307,9 |
 421,3 421,3 |
 0,22 0,22 |
 0,46 0,46 |
164 Superior |
| LLC SODEXO EUROASIA INN 7722267655 Moscow |
 1 777,1 1 777,1 |
 2 529,2 2 529,2 |
 102,0 102,0 |
 64,2 64,2 |
 0,63 0,63 |
 0,38 0,38 |
285 Medium |
| LLC AMREST INN 7825335145 St. Petersburg (Pizza Hut, KFC) |
 1 651,1 1 651,1 |
 2 167,5 2 167,5 |
 -26,7 -26,7 |
 48,8 48,8 |
 0,37 0,37 |
 0,37 0,37 |
238 Strong |
| LLC ROSINTER RESTORANTS INN 7737115648 Moscow (SHIKARI, COSTACOFFEE, ROSINTER RESTORANTS HONORED GUEST, PLANETA SUSHI, PATIO, PLANETA VOSTOK) |
 5 152,4 5 152,4 |
 6 931,1 6 931,1 |
 101,4 101,4 |
 -355,8 -355,8 |
 0,20 0,20 |
 0,18 0,18 |
208 Strong |
| LLC COFFEE HOUSE INN 7704207300 Moscow |
 2 501,1 2 501,1 |
 3 351,0 3 351,0 |
 -124,9 -124,9 |
 -45,5 -45,5 |
 -0,32 -0,32 |
 0,12 0,12 |
302 Adequate |
| JSC KOMBINAT DOSHKOLNOGO PITANIYA INN 7726221073 Moscow |
 1 005,4 1 005,4 |
 1 697,0 1 697,0 |
 6,8 6,8 |
 1,2 1,2 |
 0,24 0,24 |
 0,06 0,06 |
170 Superior |
| LLC MOSKOVSKII SHKOLNIK INN 7713213445 Moscow |
 928,4 928,4 |
 1 986,0 1 986,0 |
 2,1 2,1 |
 1,3 1,3 |
 0,08 0,08 |
 0,03 0,03 |
221 Strong |
| Average value for TOP-10 companies |  5 056,1 5 056,1 |
 7 250,1 7 250,1 |
 331,8 331,8 |
 491,7 491,7 |
 0,34 0,34 |
 0,39 0,39 |
|
| Average industry value |  101,2 101,2 |
 131,2 131,2 |
 4,9 4,9 |
 6,1 6,1 |
 0,49 0,49 |
 0,45 0,45 |
|
 growth of indicator in comparison with prior period,
growth of indicator in comparison with prior period,  decline of indicator in comparison with prior period
decline of indicator in comparison with prior period
The average value of solvency ratio of TOP-10 companies is lower than ТОP-1000 value. Three companies have the ratio higher than the recommended value and four companies improved the results in 2011 in comparison with 2009.
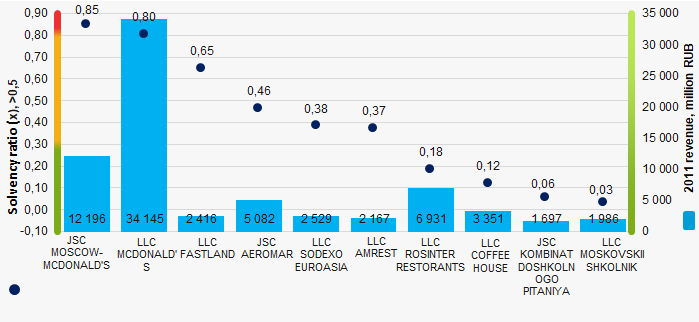 Picture 1. Solvency ratio and revenue of the largest Russian public catering companies (ТОP-10)
Picture 1. Solvency ratio and revenue of the largest Russian public catering companies (ТОP-10)Within 5 years, the average values of solvency ratio of TOP-1000 are below the recommended value with a slight upward trend (Picture 2).
 Picture 2. Change in average values of solvency ratio of TOP-1000 Russian public catering companies in 2006 – 2011
Picture 2. Change in average values of solvency ratio of TOP-1000 Russian public catering companies in 2006 – 2011TOP-10 countries by space launches
The space is still one of the key engines of the technical progress, which is available only for a few countries having necessary scientific and industrial base and budgeting. Developments of the space industry affect each person’s life, and form the country’s image and future economy.
Throughout the history of space exploration beginning from October 4, 1957 when the USSR first developed, organized and launched artificial satellite, only 10 countries joined the space race: the USA, China, European Union (without breakdown by countries), India, Japan, Iran, Republic of Korea, Israel, Democratic People's Republic of Korea and Australia. Australia had successful launches in 1967-1971, but then the national space program was scrapped.
Russia is still leading in space exploration: there are 3 300 launches of payload rockets or 56% of total launches. The USA’s share is 30%, and China’s – 6% (see Picture 1). Russia has been keeping the leadership over the past 10 years: there were 273 launches from 2010 to 2019; the second are the USA with 221 launches, and China with 216 launches is the third (see Table 1).
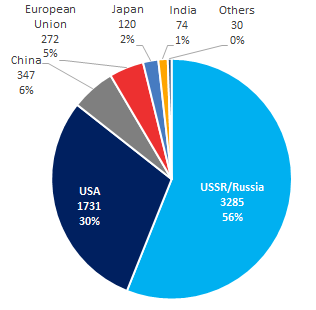 Picture 1. Total number of launches by countries, 1957-2019
Picture 1. Total number of launches by countries, 1957-2019Picture 2 shows China’s active joining the great space powers. Not that long ago, the country lagged far behind Russia and the USA, and in 2018-2019 it became first by the number of launches.
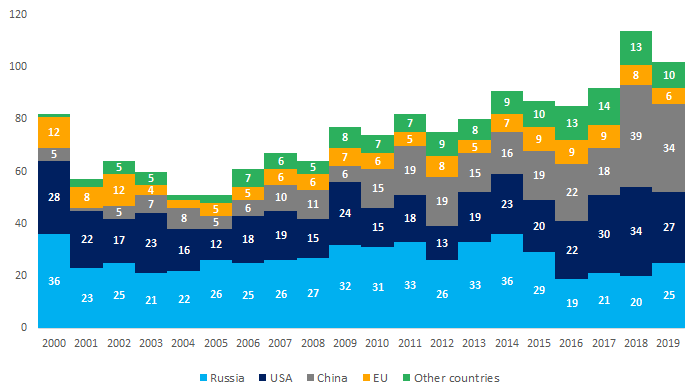 Picture 2. Dynamics of space launches by countries in 2010-2019 2000-2019
Picture 2. Dynamics of space launches by countries in 2010-2019 2000-2019Over the past ten years, an increase in the number of emergency and partial emergency launches is recorded in the Russian space program – 6,6% of total launches, that is slightly higher than in the USA (2,7%) and China (4,2%). In 2019, all 25 launches were under normal conditions for the first time since 2003.
| Country | 1957-1969 | 1970-1979 | 1980-1989 | 1990-1999 | 2000-2009 | 2010-2019 | ||||||
| З* | E** | З | E | З | E | З | E | З | E | З | E | |
| USSR/Russia | 449 | 18,5% | 909 | 5,5% | 954 | 3,6% | 434 | 5,3% | 263 | 4,9% | 273 | 6,6% |
| USA | 579 | 19,7% | 280 | 7,5% | 162 | 9,3% | 295 | 7,1% | 194 | 3,6% | 221 | 2,7% |
| China | 0 | - | 13 | 38,5% | 15 | 6,7% | 39 | 15,4% | 64 | 4,7% | 216 | 4,2% |
| European Union | 4 | 25% | 10 | 30% | 26 | 15,4% | 92 | 5,4% | 68 | 2,9% | 72 | 2,8% |
| India | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 5 | 60% | 7 | 42,9% | 16 | 12,5% | 45 | 6,7% |
| Japan | 4 | 100% | 17 | 17,6% | 23 | 0% | 17 | 17,6% | 22 | 9,1% | 37 | 2,7% |
| Iran | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 2 | 50% | 9 | 55,6% |
| Republic of Korea | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 4 | 50% |
| Israel | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 3 | 33,3% | 3 | 33,3% | 3 | 0% |
| Democratic People's Republic of Korea | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 1 | 100% | 2 | 50% |
Source: Gunter's Space Page, State Space Corporation ROSCOSMOS, calculations by Credinform
Notes to Table 1: *З – number of space launches, **E – share of emergency and partial emergency.
Before the American Crew Dragon was launched on May 30, 2020, Russia was the only country have been implementing successful and accident free piloted program on the International Space Station (ISS) over the past 9 years.
Some media credit the private company with the American space launches, and proclaim the advent of the space age 2.0. It is fair to say that the private manned spaceflights are not private as the media stated: Elon Musk’s SpaceX is funding by the government. In 2014, over 3,1 billion US dollars were allocated from the budget to implement the project, and NASA is a constant customer.
As a comparison: the budget of the State CorporationROSCOSMOS for 2020 is estimated at 2,6 billion US dollars at a current exchange rate (176 billion RUB, excluding the defense order).