Moratorium on bankruptcy is back to Russia
In Russia, Government Decree No. 497 dated March 28, 2022 introduced a moratorium on initiating bankruptcy proceedings at the request of creditors. It will be valid for the next six months - from April 1, 2022 to October 1, 2022. The moratorium applies to citizens, individual entrepreneurs and all legal entities. An exception is made only for developers from the Unified Register of Distressed Objects and persons who refused to apply the moratorium. At the same time, debtors have the right to initiate voluntary bankruptcy, if they realize that they will not be able to fulfill their obligations.
Such a business support measure also has a downside - excessive use by debtors who are not going to fulfill their obligations, hiding behind a moratorium, which in the end may affect the state of bona fide creditor.
Therefore, in the current conditions, any agreements should be preceded by a thorough check of the counterparty and all the circumstances of the counterparty’s past and present:
- financial condition and tax burden;
- arbitration cases and cases in courts of general jurisdiction;
- claim load and payment arrears;
- status of pledge and leasing agreements;
- presence of terminated public procurement transactions
etc.
The Information and Analytical system Globas assists early warning of unfair counterparties and helps to reduce risks using over 120 verification criteria.
Globas shows whether a counteprarty has signs of insolvency, information about the application of a moratorium on bankruptcy, facts of delayed payments, overdue pledges, participation in legal proceedings, both arbitration and general jurisdiction courts. Upon completion of the verification procedure, you can download a report that is customized according to your criteria. We also recommend putting your counterparties on monitoring: Globas will notify of important changes in the activities of counterparties by e-mail and in your Globas Personal Account.
About moratorium
For the first time, business owners heard about a moratorium on bankruptcy in 2020. When Russian entrepreneurs began to lose income during the period of restriction of business activity.
Effective April 3, 2020, the Federal Law No. 127-FL “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” was supplemented with Article 9.1. Moratorium on initiating bankruptcy proceedings. The right to introduce a moratorium and determine the duration of its validity is assigned to the Government of the Russian Federation. The main goal of the moratorium is to ensure economic stability within the country. In 2020, the moratorium was introduced for six months: from April to October, and was later extended until January 2021.
Since April 1, 2022, the second moratorium on bankruptcy has been in effect in the Russian Federation, introduced by the Government Decree No. 497 dated March 28, 2022. Its goal is to help improve the financial situation of companies and adapt business owners to new economic conditions. The refusal of foreign contractors to cooperate, sanctions and the complicated geopolitical situation have put Russian entrepreneurs in a difficult position. No suppliers and buyers, new markets have not been explored, revenues are falling and debts are rising. The development of this scenario could inevitably lead to a wave of bankruptcies.
Comparison of two moratoruims
| Moratorium on bankruptcy | 2020 Government Decree No. 428 dated April 3, 2020 |
2022 Government Decree No. 497 dated April 1, 2022 |
| Conditions of application |
|
|
| Exceptions | Business entities the activities of which were not classified as affected sectors of the economy. | Developers, apartment buildings and other real estate included in the Unified Register of Distressed Objects. |
To start applying the moratorium on bankruptcy, you do not need to submit special applications or confirm the type of activity. The moratorium automatically applies to all economic entities in Russia, except for unscrupulous developers.
Rules coming into force during the moratorium
1. Claims of creditors are not considered by the court, but are returned back to the applicant. The return of the application does not preclude re-applying to the court. If the moratorium expires and the debtor is unable to restore solvency by that time, the creditor has the right to re-apply for bankruptcy.
2. Fines, penalties and interest for use of another's money are not charged (does not apply to interest on a loan).
3. The moratorium applies only to bankruptcy applications. One can collect a debt through lawsuits on general terms. However, if the delay under the contract falls during the period of the moratorium, it will not be possible to recover it.
4. If there are signs of insolvency, there is no obligation to apply to the court for voluntary bankruptcy.
5. Enforced recovery for enforcement proceedings is suspended. However this does not mean that courts and other authorities cease to issue writ of execution, and bailiffs to initiate enforcement proceedings on them. Enforced recovery will begin after the end of the moratorium. The rule does not apply to arrests, recovery of wages, alimony, severance payments and penalties due to harm to life and health though.
Waiver of moratorium on bankruptcy
In addition to the advantages of applying a moratorium, there are also significant limitations:
- the shareholders of the debtor cannot distribute profits among themselves, and the participants cannot receive dividends and income by shares;
- the debtor's obligations cannot be repaid by offset if this changes the order of creditors;
- a shareholder of the company cannot leave it and ask to pay the cost of the share in cash.
Therefore, as in the period of the first moratorium on bankruptcy, it can be waived. In this case, all restrictions are removed from the applicant and the bankruptcy procedure can be initiated as usual (independently or through creditors). The waiver is made through the Unified Federal Register of Legally Significant Information by publishing a corresponding message.
Globas analyzes all messages of business entities in public registers. If a company, individual entrepreneur or citizen declares a waiver to apply the moratorium on bankruptcy, a corresponding marker appears in Globas.
Pros and cons of a moratorium on bankruptcy
The moratorium on bankruptcy allows you to improve the financial position of the company and rebuild the business model for the new economic reality. However, the moratorium may have a negative impact on the creditors themselves, who expect to receive payment for a product or service in the near future. Late payment and the inability to recover money from the debtor can disrupt the financial stability of creditors, provoking a delayed increase in bankruptcy cases.
| In Globas you can check which of your counterparties are already going through bankruptcy proceedings, which partners are in an unstable financial situation and apply a moratorium, and which ones have waived this support measure. All bankruptcy information is available in the profile of a company, individual entrepreneur or natural person. If you are not a Globas subscriber yet, fill out an application for trial access and check if there are any unreliable counterparties in your portfolio which are not going to fulfill their obligations. APPLICATION FOR GLOBAS TRIAL |
Globas helps to work under sanctions
Thousands of Russian enterprises are under sanctions. For participants in international transactions, cooperation with such companies implies the emergence of a compliance risk and may lead to the blocking of the transaction by foreign banks. At the same time, restrictions are also applied to companies controlled (more than 50%) by an entity under sanctions, even if the companies are not directly included in the list of sanctions.
When checking the counterparty, it is important to make sure that the transaction with a Russian business partner does not carry risk and will not lead to fines or even criminal liability.
Given the scale of the restrictions applied, compliance with sanctions imposes a serious burden on business. Therefore, in the current conditions, when developing Globas, we focused on the operational implementation of tools that will help to support your business and remove routine work from specialists conducting counterparty checks.
A new report, Sanctions risks, has been added to Globas. The report helps to automate the sanctions verification processes.
New tools allow to:
- verify legal entities, sole proprietors, divisions and persons for entry into the sanctions lists of the UN Security Council, Russia, the USA, the European Union, Great Britain, Switzerland, Canada, Japan, Australia, Ukraine;
- check companies for secondary sanctions (50 Percent Rule);
- check whether the company has managers and shareholders under sanctions and restrictions;
- verify affiliated companies for sanctions risk;
- get a printed report and set of documents on the performed check.
Our experts have already installed all the necessary settings for the Sanctions risks report in users' accounts. Optionally, you can adjust the verification criteria, activities, sources, summary and final Report type in accordance with corporate regulations.
Currently, connecting to the service does not require any extra fee or the need to enter into an additional agreement. The report on Sanctions risks is available as the part of the current subscription to Globas, including for new subscribers.
In our Newsletter you can find answers for questions: what sanctions are mandatory for Russian entities? Which countries are beneficiaries of the introduction of new restrictions?
Sanctions in numbers
The Russian entities are obliged to comply only with the sanctions of Russia itself and of the UN Security Council, of which Russia is a permanent member, thereby coordinating the introduction of restrictions.
At the same time, depending on the specifics of the business, it is necessary to take into account the presence of sanctions risks for many companies and individuals. For branches of foreign entities, banks, non-residents of the Russian Federation and companies that have contracts with foreign partners and conduct settlements in foreign currency, checking for sanctions risks becomes a necessary measure.
Since the end of 2021, the global sanctions rhetoric has been gaining momentum.
Currently, the most discussed types of sanctions are blocking and sectoral. Blocking sanctions prohibit any trade transactions with specific individuals and legal entities. All property of legal entities and individuals under blocking sanctions is considered "frozen" and cannot be used.
Sectoral sanctions prohibit transactions in certain sectors of the economy. For instance, a ban on the supply of weapons and dual-use goods, restricting access to the foreign capital market for companies in the energy sector.
The beneficiaries of the introduction of new sanctions and restrictions are the United States, the European Union and the United Kingdom, once in a while introducing new restrictive measures several times a day.
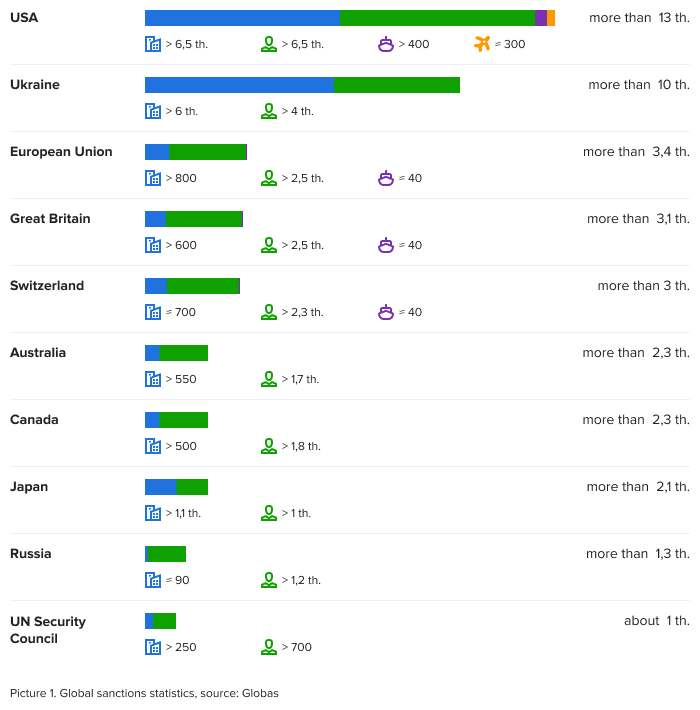
For the entire duration of the sanctions regimes of various countries, the number of companies, persons, air and water transport that have been sanctioned has exceeded 42 thousand. Of these, over 2,6 thousand Russian companies have been directly sanctioned.
The United States lead in the number of restrictions imposed: more than 13 thousand entities are under direct sanctions. Such a large number of restrictions is explained by the fact that in the United States, sanctions and restrictions are imposed by several government departments at once.
This is followed by Ukraine – over 10 thousand restrictions.
Russia has currently imposed restrictions on 1,332 entities.
Sanctions check
There is no unified consolidated global sanctions list. The departments of each country and international organizations make their own list in the national language. Sometimes information is published only in printed pdf format, which makes it difficult to verify. Therefore, an independent search is very labor-intensive and does not guarantee an accurate test result.
At the conclusion of the transaction, high-quality and fast verification of suppliers and manufacturers of goods on the sanctions lists is a necessity. The company's assets can be blocked for a single deal with a company included in one of the sanctions lists.
| Now we can offer you an automated check against global sanctions lists in the Information and Analytical system Globas. All information on sanctions risks is available in the company report. If you do not have Globas access yet, apply for a free trial, and check if your counterparties are in the sanctions lists. Free trial request |