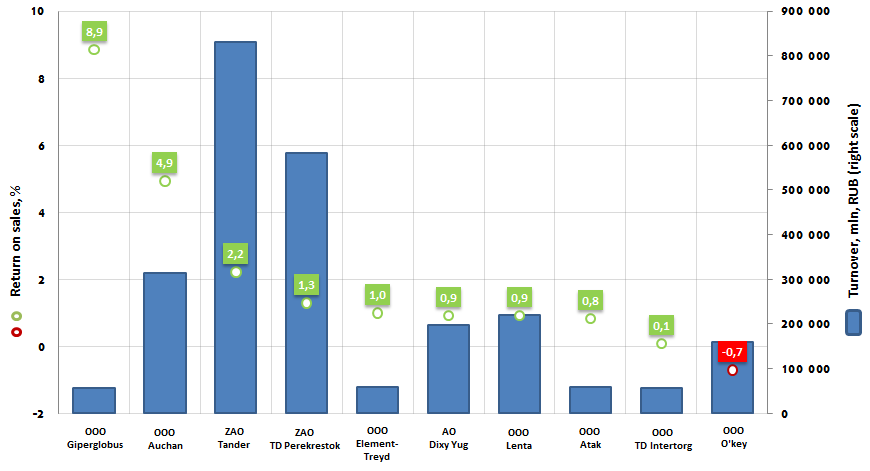
Return on sales of the Russian largest retail chains
Information agency Credinform prepared the ranking of the largest food chains in Russia.
The enterprises, taken for the ranking, are the largest by annual revenues volume in the last available in the Statistical register financial period (2014). They were ranked in descending order of the return on sales values.
Return on sales (%) shows the share of the operational profit in company’s sales result.
The ratio designates the effectiveness of the industrial and commercial activity and shows the amount of the company’s net profit on sale of RUB 1. In other words, the amount of assets after covering the products cost, payments of interests on credits and tax payments. Return on sales indicator designates the most important activity aspect – sale of basic products. Besides, it makes it possible to estimate the prime cost share in sales.
Return on sales is an indicator of the company’s price policy and its ability to control the outlays. The differences in the competitive strategies and product ranges generate significant variety of return on sales values in several companies. It is frequently used for the assessment of the company’s operating efficiency. However, the return on sale of the two firms might differ a lot under the equal values of the revenue indicator, operating expenses and profit before tax, due to influence of interest payments volume on the net profit margin.
In order to get the fullest and the fairest picture of the company’s financial situation, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the mean indicator values in the industry, but to all submitted financial indicators and ratios of the company.
| № | Name | Chain | Registration region | Revenue, mln. RUB, 2014 | Return on sales, % | GLOBAS-i® solvency index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ООО Giperglobus Tax number 7743543761 |
Globus | Moscow region | 55 573,9 | 8,9 | 279 high |
| 2 | ООО Auchan Tax number 7703270067 |
Auchan | Moscow region | 313 628,8 | 4,9 | 217 high |
| 3 | ZAO Tander Tax number 2310031475 |
Magnit | Krasnodar Territory | 830 320,2 | 2,2 | 212 high |
| 4 | ZAO Torgovy Dom Perekrestok Tax number 7728029110 |
Perekrestok | Moscow | 583 104,9 | 1,3 | 208 high |
| 5 | ООО Element-Treid Tax number 6674121179 |
Monetka | Sverdlovsk region | 57 854,3 | 1,0 | 230 high |
| 6 | АО Dixy Yug Tax number 5036045205 |
Dixy | Moscow region | 198 419,7 | 0,9 | 235 high |
| 7 | ООО Lenta Tax number 7814148471 |
Lenta | Saint-Petersburg | 220 337,8 | 0,9 | 231 high |
| 8 | ООО Atak Tax number 7743543232 |
Atak | Moscow | 58 023,0 | 0,8 | 207 high |
| 9 | ООО TD Intertorg Tax number 7842005813 |
Narodnaya 7Ya SemYA, Ideya, Norma, Spar | Leningrad region | 55 896,6 | 0,1 | 235 high |
| 10 | ООО O'key Tax number 7826087713 |
O'key | Saint-Petersburg | 158 905,3 | -0,7 | 229 high |
Return on sales of the largest food chains (Top-10) varies from 8,9% (ООО Giperglobus, Globus chain) to -0.7% (ООО O'key).
The negative return on sales in the O'key chain is an important signal to company’s management. It shows the interest of the manufacture or sales unprofitableness for each invested ruble in the product: the prime cost of products is higher than its sales profit, and the price isn’t high enough to defray all the outlays. The higher the indicator of the negative return on sales in the absolute relation is, the more the price level diverges from its effective balanced value. Moreover, the negative return on sales gives evidence that the company occupies its assets inefficiently.
According to the last published financial accounts (2014), the annual revenue of the Top-10 leaders amounted to RUB 2532,1 billion, which is higher than the indicator of the previous period by 28,4%. The revenue growth appeared to be significantly greater than the GDP growth and country’s inflation indicator for the same period.
Return on sales of the food retail market leader – ZAO Tander (Magnit chain) is higher than the nearest competitor ZAO Perekrestok has: 2,2% and 1,3% respectively.
«Magnit» is a leading retail chain in Russia by quantity of the food stores and their geographical coverage. As of June 30th, 2015 the company included 10 728 stores, of which: 8890 convenience shops, 201 hypermarkets, 110 “Magnit Family” stores and 1527 “Magnit Cosmetic” stores.
“Magnit” retail chain operates in 2233 locations in Russia. The majority of stores are located in Southern, North Caucasian, Central and Volga Federal Districts. Approximately two-thirds of stores are located in towns with the population less than 500 000 people.
The company has developed the distribution network of 29 distribution centers for more effective storage of goods and optimization of their transportation to the stores. It also owns the large fleet of 5926 vehicles which ensures an on-time goods delivery to all stores.
«Perekrestok» is a federal retail chain and one of the first city supermarket chains. This year the company celebrates a twentieth anniversary from the moment of the first store opening in Moscow in September, 1995.
The company is a leader on the Russian sale market in the supermarket format. As of September 30, 2015 the chain included 451 retail facilities, situated in 108 towns and locations in Russia.
The shopping floor space of the “Perekrestok” supermarkets numbers from 400 to 2000 square meters. The assortment amounts to 15 000 articles, including not only everyday goods, but also the luxury food from all over the world.
Nowadays the retail chain is actively at work on updating its supermarkets. The new concept of the “Perekrestok” development is intended to create conditions for the comfortable shopping environment by means of effective arrangement of the trading floor and its zoning, light and color decoration on the basis of the customers’ preferences.
These and other members of the represented ranking Top-10 of the largest food chains were assigned the high solvency index. This circumstance points at ability of the enterprises to meet the debt obligations timely and in full, the risk of nonfulfillment of which is minimal.
Individual bankruptcy – new reality for the Russian economy
The Supreme Court on September 29, 2015 has discussed the plenary meeting act on operation of the Law of December 29, 2014 that was put in force on October 1st № 476-FL «On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation to Regulate Rehabilitation Procedures for Individual Debtors».
The aim of the plenum – to give an explanation and legal objectives to the Arbitral tribunals for making fewer errors in the law enforcement practice.
According to the Supreme Court and National Association of Professional Recovery Agencies, about 200 thousand people can apply to the court for bankruptcy for the first six months of operation of the Law.
The Supreme Court clarified that courts must receive petitions on individual bankruptcy and on debts appeared before operation of the Law that is on obligations before October 1, 2015.
While in the absence of finances for bankruptcy procedure and remuneration payment to the supervisor, case may be dismissed by the court at any stage.
The question of amount of minimum required sum for financing of individual bankruptcy procedure stays open. In this case there different explanations may appear, most often not in favor of debtor. Moreover, both in the Law on Bankruptcy and in the Supreme Court clarifications, it stays unclear, how to divide, in case of bankruptcy, co-property of spouses, in repayment of this debt.
In the plenum act of the Supreme Court it`s noted that only one bankruptcy case against individual entrepreneur is permitted – physical person cannot be bankrupt as individual and as sole entrepreneur at the same time. Cases on individuals insolvency by the Arbitral tribunals are heard according to the place of the debt`s residence, that is defined by registration documents or extract of the Unified State Register of Sole Entrepreneurs. If the place of individual`s residence is unknown or is located outside Russia, such bankruptcy cases are heard by the court according to the last place of debtor`s residence in the RF.
Court costs of case on debtor`s bankruptcy and costs on payment for supervisor are paid on count of debtor`s property. If individual himself applies to the court for bankruptcy, he pays an amount (10 th RUB) into court`s deposit, also supplies with evidential document proving existence of property for repayment on the bankruptcy case. If bankruptcy is initiated by creditor, he pays recompense to financial manager, but spent money can be repaid in case of finding debtor`s property, notes the Supreme Court.
Restructuring of the debt plan must be approved on the first creditors` meeting but the court can confirm it without such approval if gets debtor`s agreement. As an exception court can do without debtor`s agreement if the debtor abuses his rights, for example, having high salary and insisting on the fastest discharge of bankruptcy. It is noted in the Supreme Court paper that court cannot confirm restructuring of the debt plan, if it is beforehand unenforceable or does not stipulate for financing for living of debtor and his family at the lesser of living wage. The plan cannot be also approved if on completing the realization period debtor is not able to settle with prospective creditors (due date to those does not come about yet). Maximum term of the plan realization is three years.
Thus,absolute majority of individuals bankruptcy procedures will become property realization procedures while payment in full discharge on the part of individuals who were not able to pay debts before that, seems to be unlikely; moreover under conditions of high interest rate (key rate of the Central Bank of the RF), preventing from refinancing of the financial obligations under more profitable conditions.