TOP-10 countries by space launches
The space is still one of the key engines of the technical progress, which is available only for a few countries having necessary scientific and industrial base and budgeting. Developments of the space industry affect each person’s life, and form the country’s image and future economy.
Throughout the history of space exploration beginning from October 4, 1957 when the USSR first developed, organized and launched artificial satellite, only 10 countries joined the space race: the USA, China, European Union (without breakdown by countries), India, Japan, Iran, Republic of Korea, Israel, Democratic People's Republic of Korea and Australia. Australia had successful launches in 1967-1971, but then the national space program was scrapped.
Russia is still leading in space exploration: there are 3 300 launches of payload rockets or 56% of total launches. The USA’s share is 30%, and China’s – 6% (see Picture 1). Russia has been keeping the leadership over the past 10 years: there were 273 launches from 2010 to 2019; the second are the USA with 221 launches, and China with 216 launches is the third (see Table 1).
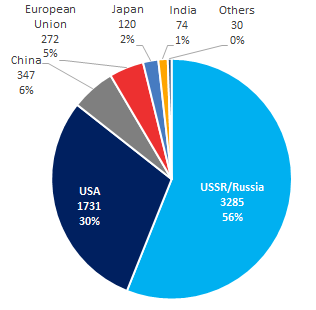 Picture 1. Total number of launches by countries, 1957-2019
Picture 1. Total number of launches by countries, 1957-2019Picture 2 shows China’s active joining the great space powers. Not that long ago, the country lagged far behind Russia and the USA, and in 2018-2019 it became first by the number of launches.
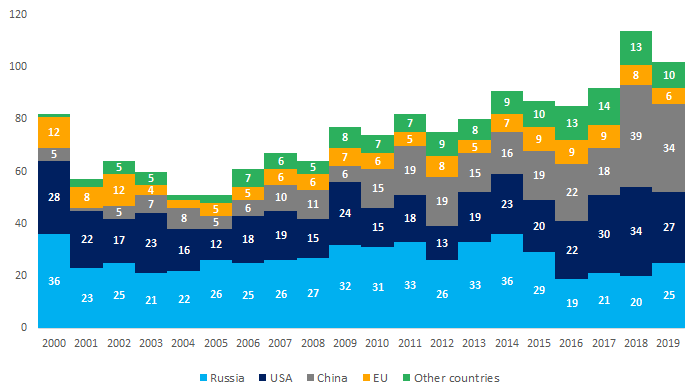 Picture 2. Dynamics of space launches by countries in 2010-2019 2000-2019
Picture 2. Dynamics of space launches by countries in 2010-2019 2000-2019Over the past ten years, an increase in the number of emergency and partial emergency launches is recorded in the Russian space program – 6,6% of total launches, that is slightly higher than in the USA (2,7%) and China (4,2%). In 2019, all 25 launches were under normal conditions for the first time since 2003.
| Country | 1957-1969 | 1970-1979 | 1980-1989 | 1990-1999 | 2000-2009 | 2010-2019 | ||||||
| З* | E** | З | E | З | E | З | E | З | E | З | E | |
| USSR/Russia | 449 | 18,5% | 909 | 5,5% | 954 | 3,6% | 434 | 5,3% | 263 | 4,9% | 273 | 6,6% |
| USA | 579 | 19,7% | 280 | 7,5% | 162 | 9,3% | 295 | 7,1% | 194 | 3,6% | 221 | 2,7% |
| China | 0 | - | 13 | 38,5% | 15 | 6,7% | 39 | 15,4% | 64 | 4,7% | 216 | 4,2% |
| European Union | 4 | 25% | 10 | 30% | 26 | 15,4% | 92 | 5,4% | 68 | 2,9% | 72 | 2,8% |
| India | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 5 | 60% | 7 | 42,9% | 16 | 12,5% | 45 | 6,7% |
| Japan | 4 | 100% | 17 | 17,6% | 23 | 0% | 17 | 17,6% | 22 | 9,1% | 37 | 2,7% |
| Iran | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 2 | 50% | 9 | 55,6% |
| Republic of Korea | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 4 | 50% |
| Israel | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 3 | 33,3% | 3 | 33,3% | 3 | 0% |
| Democratic People's Republic of Korea | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 | 100% | 1 | 100% | 2 | 50% |
Source: Gunter's Space Page, State Space Corporation ROSCOSMOS, calculations by Credinform
Notes to Table 1: *З – number of space launches, **E – share of emergency and partial emergency.
Before the American Crew Dragon was launched on May 30, 2020, Russia was the only country have been implementing successful and accident free piloted program on the International Space Station (ISS) over the past 9 years.
Some media credit the private company with the American space launches, and proclaim the advent of the space age 2.0. It is fair to say that the private manned spaceflights are not private as the media stated: Elon Musk’s SpaceX is funding by the government. In 2014, over 3,1 billion US dollars were allocated from the budget to implement the project, and NASA is a constant customer.
As a comparison: the budget of the State CorporationROSCOSMOS for 2020 is estimated at 2,6 billion US dollars at a current exchange rate (176 billion RUB, excluding the defense order).
Unified Federal Register of Population Data
The Federal law of June 8, 2020 No. 168-FL provides the formation of the Unified Federal Information Register Containing Data on the Population of the Russian Federation (hereinafter “the Register”).
The law came into force since June 8, 2020. Its certain provisions will be implemented since January 1, 2024 and January 1, 2025. In addition, there is a transition period up to December 31, 2025, and the Register may not be required by the legislative acts as a single and obligatory source of data up to January 1, 2023.
The Register will contain the following data on citizens:
- first, last and middle name;
- date and place of birth;
- gender;
- individual insurance account number (SNILS);
- individual tax number (INN);
- citizenship;
- marital status.
The Federal Tax Service is responsible for the maintenance and data security of the Register. The Register will be based on information containing in the Federal Tax Service, Ministry of Internal Affairs, Ministry of Defense Ministry of Education and Science, and state non-budgetary funds.
Data on taxes and incomes, pension, health condition and other biometric data will not be included.
State administration bodies will have access to the Register as part of their remit. Notary offices will not have direct access. However, they will be obliged to check data upon request when notarizing.
In case of discovering a mistake, the adopted law determines the procedure of introduction of amendment to the Register upon the application of the citizens. Removal of records from the Register is not provided.
The Unified register is expected to promote more accurate forecasts of the country’s development and promptly manage the ongoing processes.