Responsibility for errors in accounting increased
In April 2016 the Federal Law №77-FL as of 30.03.2016 "On Amendments to the Code of Administrative Offences of the Russian Federation" came into force.
Articles 4.5, 5.11, 29.9 and 81 of the Code of Administrative Offences (hereinafter – the Code) were amended. Administrative responsibility for repeated serious violation of requirements to accounting, including financial accounts, was implemented by the law.
The list of violations considered as serious was significantly extended. Now it includes also the following:
- registration in the accounting register of the fake business factor, as well as fake or pretended object for accounting;
- account management beyond accounting registers;
- preparation of financial statements based on the data not from the accounting registers;
- the absence of primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statement within the established document retention periods. This also applies to audit reports concerning financial statement in cases of mandatory audit.
Amounts of fines were also significantly increased. If earlier the fine for public individuals amounted to 2 – 3 thousand RUB, now it varies from 5 to 10 thousand RUB. Repeated offence will be fined at a rate from 10 to 20 thousand RUB or lead to disqualification from 1 to 2 years.
The limitation period for imposition of administrative sanctions for accounting law violation is increased to 2 years since the day of offence. The Code regulations on prolongation of the limitation period are applied to violations committed on or after April 10, 2016, and also on continuing violations disclosed since the mentioned date. Previously the limitation period was one year, because disregard of accounting maintenance rules was considered as violation of fiscal legislation. According to the current legislation, in case of expiry the limitation periods the administrative proceedings cannot be commenced and the already commenced proceeding has to be terminated.
The necessity of measures on harsher the punishment for accounting violations is clear at comparing the data of the Federal tax service on collection of taxes, fees and other mandatory payments, fiscal, penalties and tax sanctions debts to the budget system and on the number of violations detected during the desk audits (Pictures 1, 2, 3).
Picture 1. Assessment and payment of taxes, duties and other mandatory payments to the budget of the Russian Federation
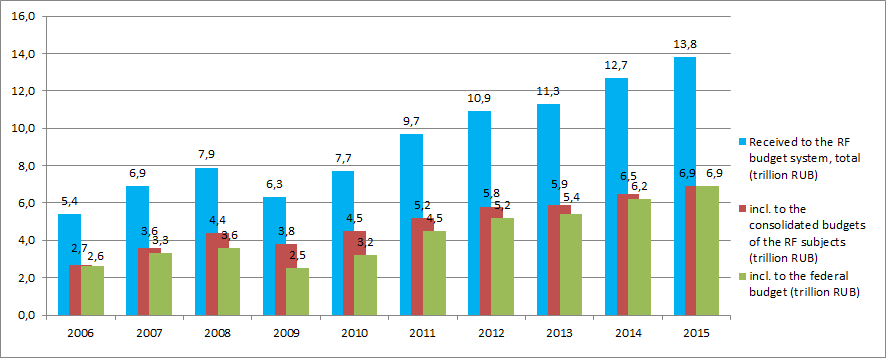
The analyses indicates that the fiscal revenues distribution structure changes with more than one and a half increase of revenues to the budget of Russia for 10 years in general. The share of regional budgets revenues decreased by no 2015 9% in comparison with 2010 is reducing.
Picture 2. Fiscal, penalties and tax sanctions debts to the budget system of the Russian Federation
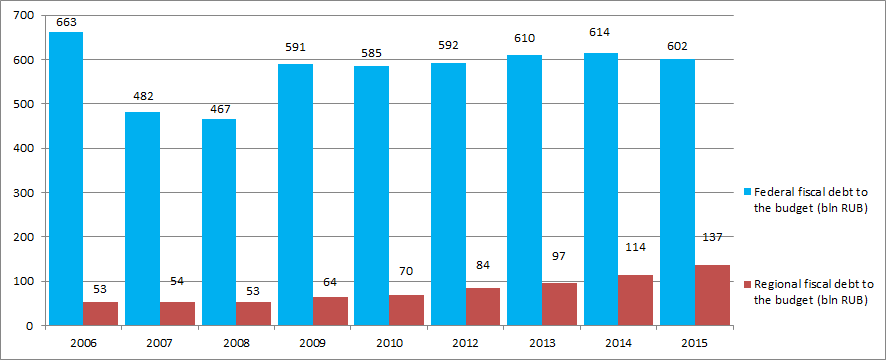
At the same time, the increase of the fiscal debt to the federal budget by 3% in comparison with 2010 is observed, as well as the debt to the regional budget is increased by 95% for the same period.
Picture 3. Number of conducted desk audits detected violations – total for the Russian Federation
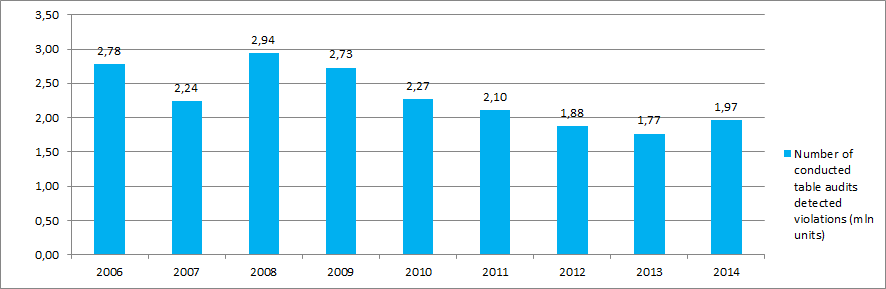
Moreover, there is a discernible trend of tax legislation violations typical for difficult economic conditions, as it was in 2008. The number of violations still remains high. Nearly every second taxpayer has violations detected during the table audits.
On difficulties of decision-making in economic policy
At the end of the first quarter of 2016 the decline of the Russian economy slowed down. This tendency has been observed since mid-2015 and, as seen, remained in the first quarter of 2016. This fact allowed the head of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade to state that Russia's economy was out of recession as early as in the 3rd quarter of 2015. According to estimates of the establishment, the GDP fell by only 0.2% in the first quarter of 2016, excluding seasonal factor, compared to the fourth quarter of 2015 and it is better than believed.
It is expected that industrial production will show a positive result at the end of the current year. Among branches the following are banked on: the food industry, oil and gas chemistry, production of mineral fertilizers, certain types of equipment. Despite positive expectations, not all is so clearly: it would seem, an increase in balanced profit of companies by 53% in 2015 was to be the impact for economic growth, but at the same time investment has fallen and continues to fall.
It is believed that the success can be obtained when specific final goals are singled and reached, such as: to achieve the inflation of 4%, to keep the budget deficit at 3% of GDP, to distribute funds to cash-strapped parties through emission. However, as practice shows, nether the tightening of monetary policy (tight control of costs and revenues of the budget) nor an infusion of emission funds will not stimulate the growth of the Russian economy.
According to specialists, we need «a complex and intelligent economic policy» and the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade sees its implementation through a solution of the following large-scale problems:
1. Creation of an investment resource.
It is meant not so much the conditions for investment, as the formation of environment for cost-saving by companies, and as the result their income will increase. The first steps should be limitation of monopolies’ tariffs and reduction of administrative costs of the business.
2. Direct funds of the resources to real investment.
In solving this problem the use of provisioned resources for other purposes causes a serious concern, for example, their withdrawal abroad that falls under the concept of «capital outflow» or «warehousing» on own accounts, which will lead to an increase in short-term assets. Such a situation can be avoided by a high level of trust between the business and government agencies, as well as improving of the business climate in general.
3. Use of special instruments of support.
Under these instruments are considered: project financing, public-private partnership. By project financing is meant a target credit for the realization of an investment project, by this the return of provisioned funds occurs from money income received in the course of its development. Public-private partnership - on the one hand, is a form of interaction between government and business, on the other hand, joint investment on mutually advantageous terms for solution of important tasks.
4. Demand creation for the production of Russian companies.
Domestic demand for domestic products is proposed to form at the expense of support for import substitution projects, external - by supporting of non-resource export.
Adopting a responsible macroeconomic policy, the implementation of internal structural changes, reducing barriers to business, the predictability of the fiscal burden, capital market development, the protection of property rights, non-raising of taxes, retrenchment, restraint in the rise in tariffs - all of this, as expected, should stimulate the growth of the economy.