Damage, bankruptcy, debts: what CEO is responsible for
Russian legislation contains many norms on the basis of which the head of a company can be brought to responsibility. This possibility is prescribed in the Civil Code, the Code of Administrative Offences, the Criminal Code.
CEO is responsible for the management decisions made, for the actions of employees and business reputation of the company. In case of incorrect actions that have caused losses or damage to the organization, the shareholders, counterparties or government agencies can initiate bringing to responsibility. In some cases, the head of an organization is brought to responsibility even after leaving the post.
TYPES OF RESPONSIBILITY
CEO's personal responsibility can be internal and external.
One of the examples of internal responsibility: CEO is responsible to the shareholder for losses incurred as a result of incorrect management decisions. As a result of his or her actions, disciplinary or financial responsibility may follow.
External types of responsibility may include subsidiary, administrative and criminal one. The main reason for their occurrence are:
- violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- bankruptcy;
- damage to creditors;
- submission of false information;
- unfair performance of obligations.
CONSEQUENCES
Bringing CEO to responsibility negatively affects the reliability of all legal entities under his or her management. Interaction with unreliable organizations may attract attention from the Federal Tax Service of Russia. The regulator may regard such transactions as fictitious and apply penalties in the form of additional taxes, criminal proceedings and even removal of the company from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Responsibility in such cases falls on CEO or the decision-making person.
CHECK IN GLOBAS
To avoid such a scenario, it is necessary to exercise commercial due diligence. The Information and Analytical system Globas helps to identify signs of shell companies and unreliable organizations, including negative factors concerning the company's CEO.
Let's consider cases when Globas will help to identify the personal responsibility of CEOs.
Case 1
Identification of facts of violations of the legislation of the Russian Federation
In the compliance requirements of many enterprises, there is a clause on the inadmissibility of cooperation with companies related to violations of the laws of the Russian Federation. In case of interaction with the violator, a large fine or criminal liability may be imposed.
Signing a fictitious contract, for instance, for the purpose of understating the tax base provides for a fine of up to 1 million RUB or imprisonment for up to 10 years.
For non-payment of taxes, CEO faces a fine of 500 thousand RUB and imprisonment for up to 6 years.
For giving bribes, liability is provided in the form of a fine of 2,5 million RUB and imprisonment for up to 8 years.
When analyzing a business partner in Globas, information about bringing to administrative and criminal responsibility, participation in court proceedings, inclusion in the lists of official authorities is displayed automatically. It is also available to request information about the arrears, fines or penalties, search for enforcement proceedings and suspicion of committing crimes. All information is displayed in the "one window" mode.
Case 2
Bankruptcy and damage to creditors
Irrational decisions and unreasonable contracts can lead to premature liquidation of the company due to insolvency. However, after the bankruptcy procedure begins, an audit will be conducted against CEO and all persons controlling the debtor. The official receiver will check for signs of intentional or fictitious bankruptcy and determine the persons responsible for causing damage to the company. If the fault is proved, the persons controlling the debtor will be brought to subsidiary responsibility or compensation for damages.
Globas contains all information about a person's entrepreneurial activity and their participation in business. Moreover, information from related sources is analyzed and compared. Globas will show a warning marker about bringing a person to responsibility in a bankruptcy case, calculate the amount of joint responsibility, show notifications from the Unified Federal Bankruptcy Register and the arbitration case related to this event.
| In the Information and Analytical system Globas, you can check which of your business partners are already undergoing bankruptcy proceedings, as well as which of them have unstable financial position. |
Case 3
False information, unfair or untimely fulfillment of obligations
Liquidation of companies in the presence of false information and debts to the budget may be resulted in the future refusal to register information about the shareholder or CEO for 3 years.
Such a refusal to make state registration to an individual may affect his or her business in the future. The individual cannot:
- become CEO or establish a new legal entity;
- make changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities related to his or her name until 3 years have passed since the entry was made;
- re-register the pledge of the share in the authorized capital.
Checking for timely fulfillment of obligations is also an integral part of the due diligence. The presence of a large number of arbitration cases on economic disputes may, for instance, characterize a partner as unfairly related to payment discipline. In the future, the growth of obligations may affect the financial position of the counterparty and lead to bankruptcy.
In Globas, the entire business history of an entrepreneur is comprehensively analyzed. In case of detection of violations of the law in any of the related companies, a note about the risk of refusal of state registration will be displayed. Counterparties unfairly related to the payment discipline can be identified using the Arbitration and Enforcement Proceedings sections. Cases with the category of improper performance of obligations will help to identify the overdue accounts payable.
|
Globas helps
to analyze business partners, minimize commercial, tax, and sanctions risks, relieve the experts conducting inspections from routine, and uses only reliable
information from official sources. If you are not yet Globas subscriber, apply for trial access and check if there are unreliable counterparties in your portfolio who are not going to fulfill their obligations. GET TRIAL ACCESS |
New challenges for business in Russia. How to work in the reality of the XXI century
International restrictions, reorientation of the global economy to the East, regular changes in legislation, large-scale sanctions, breaks in trade chains, “legalization” of parallel imports, all these factors form the new economic reality of the XXI century. The skill of successful adaptation to rapidly changing environmental conditions is the key to effectively made decisions.
Focus on the East
The sharp break in export-import relations with the European Union and Western countries, as well as the departure of large foreign companies, are forcing businesses to look for new reliable partners. The course of reorientation of the Russian economy and international trade towards the Asian direction announced at the state level creates opportunities for entrepreneurs to search for new markets and build alternative supply chains.
The geography of sanctions and restrictions against Russia is represented by the United States, the European Union, Switzerland, Great Britain, Japan, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other countries. Therefore, when planning transactions, it is worth considering the effect of not only direct, but also secondary sanctions. The US sanctions legislation, for instance, allows the introduction of restrictive measures against the participants in the transaction, if the result is the export or re-export of goods and technologies prohibited from being imported into Russia.
| Automate the verification of counterparties in Globas using the Sanctions risks report. The functionality of the report allows you to carry out a comprehensive analysis of legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, divisions and persons for inclusion in the sanctions lists, evaluate indirect and secondary sanctions, including the 50 Percent Rule. |
However, more than 80 countries around the world have not imposed sanctions against Russia. These countries are open to cooperation and development of trade and market relations. The statistics of the Information Agency Credinform confirms that the customers of business reports via Globas are now focused on companies in China, India, UAE, Turkey, Israel and CIS.
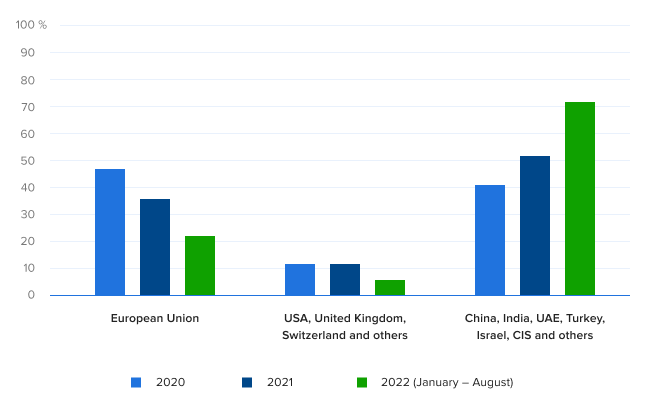 Picture 1. Distribution of business reports on foreign companies, 2020-2022
Picture 1. Distribution of business reports on foreign companies, 2020-2022Sources: Credinform, Globas
| Due to a wide network of partners, Credinform provides information
about legal entities and entrepreneurs around the world: in Asia, Africa, Europe, America and Australia. The report can be ordered individually or via
Globas. The content of the reports complies with international standards: registration data, management, shareholders, types of activities, balance sheet, income statement, comprehensive assessment of solvency. For each foreign company, the experts of the Credinform Information Department additionally search for links with Russian business. |
Parallel import
In connection with the withdrawal from Russia of a number of large foreign companies and brands, parallel import was legalized at the legislative level. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 29, 2022 No. 503.
Parallel import refers to the import of goods into the country without the consent of the right holder. According to the list of the Ministry of Industry and Trade, the import of cars, medical equipment, pharmaceutical products, household appliances and weapons into the country is allowed. A full list of products is specified in the Order No. 1532 dated April 19, 2022.
The importation of goods under parallel import imposes a number of obligations on the business. Now, only the end seller is responsible for observance of all consumer rights and fulfillment of warranty obligations. Moreover, only original goods can be imported.
| Check the supplier before the deal to protect yourself from buying low-quality goods. Globas will help to check the experience of the importer, whether it has employees and assets. As well as the attention will be paid to the courts for non-fulfillment of supply contracts, active or bad enforcement proceedings, and fines. |
Postponed effect. Why Moratorium on bankruptcy can do a disservice
Moratorium on bankruptcy, imposed up to October 1, 2022, became another anti-crisis measure to support business in Russia. The moratorium protected citizens, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities, except for the developers from the register of distressed objects and persons who refused from the moratorium.
An unobvious and negative consequence of the expiration of the moratorium may be a new wave of bankruptcies, as well as the closure of enterprises dependent on imports, and as a result, the threat of non-fulfillment of already concluded agreements and contracts.
To avoid these negative consequences, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive study of the future counterparty, check its financial position, tax burden, judicial history, the status of pledge and leasing agreements.
| In the Information and Analytical System Globas you can check which of your counterparties are already going through bankruptcy proceedings, or have unstable financial situation and at the same time apply a moratorium, and which ones have refused this support measure. |
Friendly compliance
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 81 dated March 1, 2022 introduced a special procedure for executing transactions with foreign persons from the list of unfriendly states. From March 02, 2022, transactions to which a special procedure must be applied include:
- granting credits and loans to non-residents in rubles;
- granting loans to non-residents in foreign currency;
- purchase and sale of securities and real estate to non-residents;
- transferring money without opening a bank account using foreign payment services.
The mentioned transactions are allowed only with the consent of the Government Commission for the Control of Foreign Investments in the Russian Federation. To make transactions with securities, you need to obtain permission from the Bank of Russia.
Currently, the list of unfriendly states includes 55 countries and territories. Among them: USA, UK, EU member states, Switzerland, Canada, Japan, Republic of Korea.
| Use
Globas
to check if a shareholder of a partner company is registered in a country that commits unfriendly actions against the Russian Federation. Globas users have access to ready-made reports on enterprises, where 350 criteria for full compliance control are checked. Download a ready-made report for your own company or for your counterparties and assess the risk level of the transaction. If you are not subscribed to Globas yet, fill out an application for trial access and check if there are high-risk partners among your counterparties. GET TRIAL ACCESS |