Overall liquidity of telephone operators in Russia
Information agency Credinform offers to get acquainted with the ranking of Russian telephone operators. The companies with the highest volume of revenue involved in this activity were selected by the experts according to the data from the Statistical Register for the latest available period (for the year 2012). Then, the first 10 enterprises selected by turnover were ranked by decrease in overall liquidity ratio.
Overall liquidity ratio (in foreign sources often is named as current liquidity ratio) shows company’s ability to repay current (short-term) liabilities using only working assets. This indicator is calculated as the relation of current assets to current liabilities, i.e. to short-term liabilities. According to accepted standards, a norm for this ratio is the range between 1,0 and 2,0. Lower limit arises from that it should be at least enough working assets for full satisfaction of short-term liabilities, otherwise a company will be at risk of bankruptcy. However, the reverse situation with a significant excess of short-term assets over liabilities (three-four times as much or more) is considered also to be undesired, because it can testify to the failure of capital structure, as well as to irrational or ineffective investment of funds.
| № | Name INN | Region | Turnover for 2012, in mln RUB | Overall liquidity ratio, (х) | Solvency index GLOBAS-i® |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ROSTOVSKAYA SOTOVAYA SVYAZ CJSC INN 6163025500 |
Rostov region | 7301 | 1,01 | 198 (the highest) |
| 2 | NOKIA SOLYUSHNZ END NETVORKS LLC INN 7725593720 |
Moscow | 7304 | 0,89 | 276 (high) |
| 3 | MOBILNYE TELESISTEMY OJSC INN 7740000076 |
Moscow | 270829 | 0,86 | 218 (high) |
| 4 | VYMPEL-KOMMUNIKATSII OJSC INN 7713076301 |
Moscow | 280301 | 0,85 | 238 (high) |
| 5 | TELE2-VORONEZH CJSC INN 3666036485 |
Voronezh region | 8713 | 0,73 | 252 (high) |
| 6 | TATTELEKOM OJSC INN 1681000024 |
Republic of Tatarstan | 7193 | 0,67 | 192 (the highest) |
| 7 | MEGAFON OJSC INN 7812014560 |
Moscow | 254453 | 0,64 | 216 (high) |
| 8 | TELE2-KEMEROVO CJSC INN 4207041667 |
Kemerovo region | 7228 | 0,48 | 209 (high) |
| 9 | TELE2-SANKT-PETERBURG OJSC INN 7815020097 |
Saint-Petersburg | 10113 | 0,45 | 247 (high) |
| 10 | EKATERINBURG-2000 LLC INN 6661079603 |
Sverdlovsk region | 7183 | 0,44 | 234 (high) |
The leader of the ranking, ROSTOVSKAYA SOTOVAYA SVYAZ CJSC, turned out to be the only one enterprise, which showed the overall liquidity ratio in compliance with the recommended values. Moreover, the company got the highest solvency index GLOBAS-i®, that testifies to its stable financial standing.
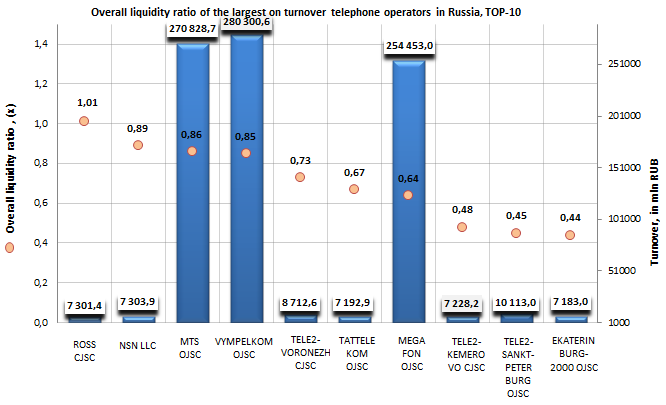
At the same time the companies NOKIA SOLYUSHNZ END NETVORKS LLC (0,89), MOBILNYE TELESISTEMY OJSC (0,86) and VYMPEL-KOMMUNIKATSII OJSC (0,85) have the values of the overall liquidity ratio, which deviate a little from recommended values, that is why it is not worth to speak of high credit risks for these enterprises. Besides, considering the combination of both financial and non-financial indicators, all three companies got a high solvency index GLOBAS-i®.
Unfortunately, the rest enterprises of the ranking showed the values of the overall liquidity ratio being essentially below the recommended lower limit, what testifies to that they have not enough working assets for full satisfaction of short-term liabilities. However, all enterprises got a high and the highest solvency index GLOBAS-i®, what points to their ability to pay off loan liabilities in time and fully.
For the growth of the overall liquidity ratio and maintenance of its minimum required value some rules must be known and observed. So, for stably high (within the normative range) overall liquidity ratio it is important the profitable operation of an enterprise, including also its growth, and financing of investment program (investments into noncurrent assets) should be accounted for long-term and not for short-term credits. Also it is necessary to aim at reasonable minimization of inventory and WIP, i.e. at decrease in the least liquid current assets.
Sanctions, embargo, food security… Who will be the most damaged?
On the 6th of August 2014 Vladimir Putin has signed, in response for sanctions from the West and with the aim of protecting of national interests of the RF, the decree about application of certain special economic measures. Thereby the President has prohibited or restricted, for one year, the import to Russia of certain kinds of agricultural products, raw material and provision from countries, which have joined the sanctions against the RF. Will such decision cripple the economy of the country?
National security protection is the most important function of the state. One of its essential constituents is food security, set forth in the relevant Doctrine, approved by the decree of the President of the RF from 30.01.2010 №120. The status of food security is evaluated in it through the test of specific weight of domestic products in the total volume of this article taking into account the import to the country. And threshold values of the indicator, set forth in the Doctrine, serve as a guidemark; it is undesirable for the economy to go below them. For example, on meat and meat products the specific weight of production should be not less than 85%, on milk and dairy products – 90%, fish products – 80%, potato – 95%.
The experts of the Information agency Credinform have estimated the volumes of output and import of food, included in the banned list, and compared the specific weight of this production with the threshold indicator, embodied in the Doctrine (s. Table 1). The production meant for baby food is excluded from calculations.
| Goods prohibited for importation into the RF | Import volume in 2013, ths tons (mln $) | Volume of output in 2013 in Russia, ths tons | Specific weight of production in the total volume of resources, % | Threshold indicator according to the Doctrine, % | Exceedance, percentage points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat (cattle and pork meat, poultry; fresh, cooled or frozen) and edible by-products | 820,9 (2 178,6) |
5 218,44 | 86,41 | 85 | +1,41 |
| Fish and crustaceans, molluscs and other aquatic invertebrates | 361,6 (1 216,2) |
3 681,5 | 91,06 | 80 | +11,06 |
| Milk and dairy products | 400,5 (1 674,6) |
12 681,8 | 96,94 | 90 | +6,94 |
| Vegetables, edible roots and tuber crops | 876,4 (927,9) |
14 689 / 44 888,0 (potato included) |
94,37 / 98,08 (potato included) |
concerning potato – 95 | +3,08 |
| Fruit and nuts | 1 425,6 (1 678,3) |
22 941,5 | 94,15 | Not specified | - |
| Sausages and similar products from meat, meat by-products or blood; ready-made meals, manufactured on their basis | 16,3 (72,0) |
2 461,0 | 99,34 | Not specified | - |
| Ready-made meals, including cheeses and quark on the basis of vegetable fats | 15,2 (31,6) |
No data | - | Not specified | - |
| Food products (milk-containing products, on the basis of vegetable fats) | 86,4 (530,1) |
No data | - | Not specified | - |
The exceedance of obligatory indicators of the Doctrine points to that Russia is able to supply its citizens with food products by itself. Embargo on import into Russia of products, mentioned in the table, won’t do harm to Russian consumers. And the introduction of sanctions, from the point of view of food security of the RF, should not cripple the economy of the country.
Moreover, existing volumes of output of products testify to the absence of grounds for the rise in prices on them. Here is no wonder, that lately it was tightened the control over the food market on the side of the Federal monopoly service of the RF, the Public Chamber and other organizations, for the purpose to detect in time and stop illegally actions of unfair retailers, aiming at driving up the prices on the back of embargo.
Under current conditions the importers, carried out the delivery of banned food products, have to reorient their business. It offers good chances for them to organize business cooperation first of all with Russian manufacturers. However, food retailers, for the purpose of cost saving, are interested in direct supplies from China or a number of countries of Asia and Southern America.
According to estimations of the analysts from Credinform, the introduced sanctions will affect most seriously the countries of the USA, Canada, Norway and Australia, but most of all – European states (s. Table 2). At year-end 2013 it was imported more than 4 mln tons of food products into Russia, for a total amount of 8,3 bln $. Considering, that on a number of estimates the import volume was to increase in 2014, then the expected forecast of the damage to economies of the countries, which have fallen under sanctions, can make up to 12 bln $.
| Country of origin | Share in import volume, % | Outgoing country | Share in import volume, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meat (cattle and pork meat, poultry; fresh, cooled or frozen) and edible by-products | |||
| USA | 15,88 | Germany | 15,41 |
| Denmark | 14,16 | USA | 15,37 |
| Germany | 12,86 | Denmark | 13,40 |
| Fish and crustaceans, molluscs and other aquatic invertebrates | |||
| Norway | 74,12 | Norway | 73,58 |
| Canada | 7,68 | Canada | 7,42 |
| USA | 5,53 | USA | 4,72 |
| Milk and dairy products | |||
| Finnland | 17,88 | Finnland | 17,91 |
| Netherlands | 15,63 | Netherlands | 17,39 |
| Lithuania | 15,30 | Germany | 11,84 |
| Vegetables, edible roots and tuber crops | |||
| Netherlands | 27,02 | Lithuania | 32,83 |
| Poland | 24,17 | Poland | 24,32 |
| Spain | 23,02 | Netherlands | 13,89 |
| Fruit and nuts | |||
| Poland | 24,56 | Poland | 25,46 |
| Spain | 18,55 | Lithuania | 15,55 |
| USA | 12,86 | Greece | 8,93 |
| Sausages and similar products from meat, meat by-products or blood; ready-made meals, manufactured on their basis | |||
| Lithuania | 23,73 | Lithuania | 25,31 |
| Poland | 13,82 | Poland | 14,86 |
| Italy | 12,34 | Latvia | 14,07 |
| Ready-made meals, including cheeses and quark on the basis of vegetable fats | |||
| Poland | 38,33 | Latvia | 34,55 |
| Germany | 29,22 | Germany | 28,54 |
| Denmark | 16,92 | Denmark | 16,92 |
| Food products (milk-containing products, on the basis of vegetable fats) | |||
| Germany | 29,62 | Germany | 20,98 |
| USA | 17,66 | Lithuania | 12,54 |
| Poland | 5,75 | Netherlands | 10,21 |
The embargo will have a high impact most of all on Norway, which imported in 2013 more than 74% of the total volume of fish products into Russia, on Poland – from the import ban of vegetables, fruit, sausages, ready-made meals and food products, on the USA – regarding deliveries of meat, fish products, fruit and food products, Germany – regarding meat, ready-made meals and food products, the Netherlands – regarding dairy products and vegetables. Lithuania and Latvia can be also considered among badly-hit countries, because a significant volume of import deliveries of different kinds of goods is carried out through their territories.