Self-regulation in the financial market of Russia
The financial market, as a combination of economic relations between sellers and buyers of cash resources and investment properties, consists of securities and gold markets, money and foreign exchange markets. Money and securities are the main subjects of trading in the financial market.
Figural comparison of finances with the circulatory system of the economy indicates the key importance of the financial market for the functioning of the state. This thesis has a remarkable confirmation by the indexes of capitalization of the Russian stock market (in December 2014 they made 338.5 billion USD), as well as the indexes of GVA volume in the financial activity for 2014 (3,2 trillion RUB). The Moscow stock exchange, the largest in Russia, taking the lead in trading volume of trading in all segments of the exchange market in FSU countries and in Eastern Europe, is among the TOP-20 world's largest stock exchanges on the trading volume on the stock market, and on the trading volume in the time market - among the TOP-10.
The dynamic development of the Russian financial market, its constant segmentation, growing variety and complication of instruments has led gradually to the occurrence of many regulators, formalization of their activities, weakening of stimulating levers of regulation compared with prohibitive.
The measures prescribed by the Federal Law of July 13, 2015 №223-FZ «On self-regulatory organizations in the financial market area and on introducing amendments to Articles 2 and 6 of the Federal Law «On introducing amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation», which becomes into force on the 11th of January 2016 (except certain provisions), are intended to overcome these problems.
The law assumes the creation of self-regulatory organizations (SRO) in all segments of the financial market, except the banking sector, i.e. it will extend to brokers, dealers and managers, depositories and specialized depositories, registrars, non-governmental pension funds, joint-stock and mutual funds, management companies of investment funds, insurance companies, insurance brokers, mutual insurance companies, microfinance institutions, credit housing and savings consumers’ co-operatives, agricultural consumer credit co-operatives, pawnbroker's offices.
The membership in SRO will be obligatory. Each segment may have two SRO, but a financial institution can be a member only of one SRO in its segment. It is possible also to establish SRO, which join financial institutions from different segments, but when certain requirements are satisfied. Supervision over the activity of SRO will be provided by the Central Bank of the RF, which will have the right to impose fines, to send a demand of the replacement of the management of SRO, to assign and revoke the status of these organizations. At the same time the Central Bank is allowed to give self-regulatory organizations a number of powers of regulation and supervision.
Self-regulatory organizations in the field of financial market are given the right to protect and represent the interests of their members in the Central Bank of the RF, federal executive bodies, local executive bodies, courts, international organizations. The development and adoption of a code of professional ethics, performance standards fall also within the scope of their activities.
Obligatory National associations of self-regulatory organizations in the field of financial market are not prescribed by the law.
The world experience in the field of self-regulation is very contradictory. In the USA, for example, there are two types of it: compulsory and voluntary, by that the joint-stock market is a matter of compulsory self-regulation. All its participants are required to be register at the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). Great Britain, in its turn, which former took the lead in terms of financial markets’ regulation worldwide, has refused to self-regulation in this area as far back as 1997 because of massive violations of the rights of investors. At the moment the activity of financial markets is controlled by the Financial Services Authority (FSA) there - a non-governmental organization with the liability limited by guarantee.
How will the self-regulation of the financial market in Russia operate - the time will tell. According to experts, already by the middle of 2016 it will be possible to assess how the measures, introduced by the new law, would influence on the efficiency of work of financial institutions.
According to the «All-Russian portal about self-regulation» in the financial sector, 22 SRO have been already registered by now. To get acquainted with their activities, as well as with performance indicators of organizations of financial and other markets is possible by subscription to the information and analytical system Globas-i®.
The dynamics of the ruble-dollar rate as a mirror of the Russian economy
According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, for the recent 2 weeks (from September 19 to October 05, 2015) the exchange rate varied from RUB 65,03 to 66,52 to US dollar (see Figure 1). However considering all the volatility of the rate the linear trend during the stated period was showing the descending curve. It gives evidence of several movements towards appreciation. Nevertheless, the strengthening of the ruble-dollar rate cannot be characterized as a stable, due to the fact that too short a time was taken for the evaluation.
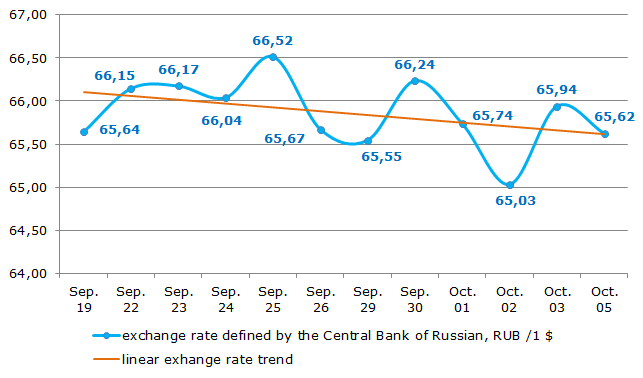
Figure 1. Ruble-dollar rate for the period of September 19 – October 05, 2015
The analysis of the average values for the period from December, 2014 to September, 2015 showed that there was a fluctuation in exchange rate in the range of RUB 50,47 – 66,78 to US dollar (Figure 2). Moreover, the average value rate curve has delicately mirrored the Russian economic environment in the whole: the January leap was a continuing reaction to the situation in December, 2014. Then from February to May, 2015 there was an appreciation of the ruble, the economy was recovering and the analysts were expecting the improvement of the business activity.
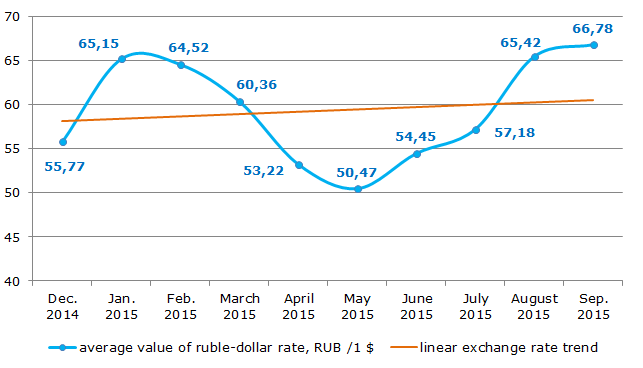
Figure 2. Monthly average value of the ruble-dollar rate for the period of December, 2014 – September, 2015
Beginning from May, 2015, the ruble started weakening gradually. In September, 2015 its average value reached RUB 66,78 for a US dollar. In that time the expectations of the experts concerning sanctions’ ending, increase in world oil market prices and improvements in the Russian economy weren’t satisfied. For example, in the end of the second quarter of 2015, the economic experts started talking about the recession in the industry and in the third quarter – about stagnation. Probably the declining ruble being influenced by different factors made it possible to soften the negative tendencies in the economy and to deny the sharp income decrease and consequently the fall-off GDP volume.
According to experts of the Information Agency Credinform, the ruble in the whole is influenced by different factors. The key factors are: geopolitical tensions; international sanctions; the environment of the American and Chinese economies; decrease in world oil market price; negative tendencies in the Russian economy; risk of deficit in currency liquidity etc.
Recently the media has proposed different ways of the ruble appreciation. There are 9 methods offered by the experts of the Sberbank CIB:
- not to buy gold,
- to put pressure on the exporters,
- interventions of the Central Bank of Russia,
- interventions of the Ministry of Finance,
- verbal interventions,
- currency repurchase agreement,
- currency repurchase agreement,
- rate increase,
- capital flow control.
The evaluation of the stated methods shows that the restrictive or proscriptive measures should be taken. The refusal of buying gold, decline in oil output, in particular putting pressure on the exporters, rate increase, capital flow control will lead to even a greater worsening of the country’s economy and to repulsion of investors. The latter is important seeing that in present conditions the economic driver might be not a consumer demand, but investments. Other financial instruments should be used carefully, in order not to cripple the country’s economy.
On the other hand, the weak ruble is sort of positive instrument to stimulate the Russian economy, due to the fact that it promotes the concentration of monetary means in Russia. For example, Russian products appear to be more rival according to value; the effectiveness of investments in the Russian economy has increased; export benefit; negative trends generated the detailed income and expense estimation and the improvement of the financial flows; the tourist movement has increased; Russian citizens give preference to vacation in Russia etc. Therefore the country’s leadership and the leading economists advise the business community and the citizens to prepare for living under the conditions of the low oil price and consequently for the prevailing ruble and US dollar rate.