Assessing the risk of a field tax audit using Globas
In the context of the new economic reality, the Government of the Russian Federation, in order to ensure financial stability and mitigate the consequences of restrictive measures, made a number of indulgences concerning tax audits:
- check on compliance with the currency legislation are suspended;
- IT companies accredited in the territory of the Russian Federation are exempted from field tax audits.
| You can check whether your company belongs to accredited IT organizations in Globas. |
It is important that the introduced relaxations affect only a part of organizations and do not exempt taxpayers from complying with tax laws. At the same time, the task of checking tax collection for the Federal Tax Service remains relevant. Despite the fact that the number of field tax audits has been decreasing in recent years, their effectiveness is growing.
In 2021, the Federal Tax Service conducted 7,765 field audits, which is 14% less than in the pre-pandemic 2019. However, as a result of such actions, the business received additional taxes of 383 billion RUB, including penalties and fines. The average cost of audit is 50 million RUB, which is almost twice as much as in 2020. At the same time, 99% of appeals to the Federal Tax Service remain unsatisfied. In arbitration courts, the tax service also wins more often.
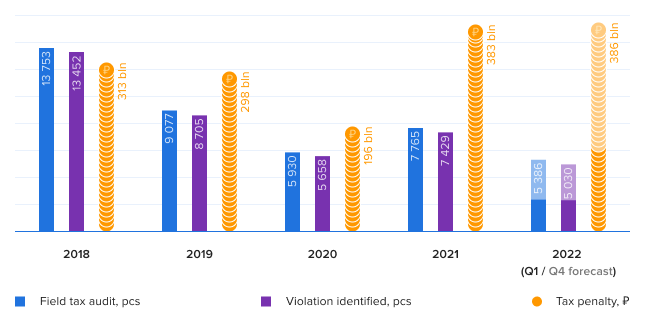 Picture 1. Results of field tax audit in 2018-2022
Picture 1. Results of field tax audit in 2018-2022Source: Federal Tax Service, Credinform forecast.
At the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum, the President of the Russian Federation emphasized the need to cancel most business inspections. The Federal Tax Service also took a course to reduce the number of inspections by increasing their quality. Taking into account the current trends at the end of the full 2022, the experts of the Credinform Information Agency predict a decrease in the number of inspections to the level of the pandemic 2020. At the same time, the effectiveness of tax penalties may remain at the level of the record 2021 year.
Types of tax audits
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are two types of tax audits: on-site and field tax audits.
Office tax audit lasts no more than three months. The tax inspector remotely analyzes the submitted declaration and evaluates the correctness of the tax calculation. If inaccuracies or contradictions are found, the missing amounts are charged for payment, fines and penalties are imposed, and a requirement to prepare an adjustment declaration may also be made.
During a field audit, the tax inspector goes to the business owner's place for a thorough examination of the reporting. The correctness of tax calculation, their timely payment and possible VAT evasion are controlled, documents on transactions with counterparties are checked. The inspection has the right to examine the company, conduct conversations with employees, analyze the activities of branches and representative offices.
In addition to the Federal Tax Service, inspectors from other services can also come to the enterprise with a field inspection.
| Check in Globas whether your company or a counterparty is included in the summary plan of inspections of the Prosecutor General's Office in order to prepare in advance for the visit of government agencies. A full list of inspections is available in Globas, and conclusions of inspectors are already available for many of them. |
Risk criteria for evaluating a field tax audit
You can reduce the risk of meeting with the tax authority as part of a field audit by taking into account the criteria that FTS inspectors follow when choosing candidates for their visit. Similar criteria should be applied to evaluate your counterparties.
Here are some of them:
- The tax burden is below the industry average.
- The average monthly wage per employee is below the industry average.
If the indicators do not correspond to the average values for the industry in the region, then the likelihood of a field tax audit increases. - Excess of expenses over income for several tax periods.
If the are constant losses, the Federal Tax Service may assume that the business owners are hiding income or a wish to liquidate the organization. - Re-registration of the taxpayer in the IFTS.
'Migration' between tax authorities can be interpreted by inspectors as an attempt to avoid inspections and evade taxation. - Conclusion of a deal with dubious counterparties.
Checking the business partner before the conclusion of the contract must be carried out and carefully recorded.
These are the main criteria that the Federal Tax Service pays attention to when planning a visit with an inspection on the enterprise. However, the full list is much longer. It was approved by order No. MM-3-06/333@ of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 30, 2007 in the form of a “Concept for the planning system for field tax audits”.
| Globas users have access to ready-made reports on enterprises, where, in addition to the official criteria of the Federal Tax Service, many indirect factors are analyzed, to which the tax inspector additionally pays attention. 90 criteria of the Federal Tax Service and 120 criteria of full compliance control are checked. Download a ready-made report for your own company or for your counterparties and assess the degree of risk of a field tax audit. If you are not a Globas subscriber yet, fill out an application for trial access and check if there are persons with increased risk among your counterparties, the cooperation with which is better to be reconsidered. |
Self-employment: opportunities for checking persons in Globas
The self–employed are a special category of taxpayers, individuals or individual entrepreneurs who have switched to a special tax regime with a reduced rate. It is also called the Professional Income Tax (PIT). Under current legislation, the tax rate for those who work with individuals is 4%, and for those who provide services to legal entities or individual entrepreneurs – 6%.
Every year the popularity of this tax regime is growing. In 2022, the number of self-employed reached 4 million people and has already exceeded the number of individual entrepreneurs.
The self-employed can provide an extensive list of jobs and services: from layout of websites and writing texts to legal advice and accounting. In cooperation with such experts, enterprises receive a number of advantages:
- exemption from payment of personal income tax, insurance premiums and pension contributions, which saves about 30% monthly from the standard salary of a full-time specialist;
- payment is made for the work done, and not for the time spent in the office, without the need to provide labor guarantees in the form of sick leave and vacations;
- the possibility of remote cooperation.
The benefits will be available only if there is a receipt confirming the payment made for the work under the contract. A bill from a self-employed person will also be needed for tax reporting to prove that the payment was made legally. If this rule is ignored, problems may arise for both the customer and the self-employed: the tax authority may suspect that illegal monetary transactions are carried out in the company, and the contractor hides income.
However, in case of violation of the legislation governing the application of a special tax regime, the customer of services may be held liable. And these mean fines, inspections and lawsuits.
| Five main rules that must be followed when agreeing a contract with a self-employed will help to build the rules for checking the self-employed and avoid risks. |
Rule No. 1: don't hire former employees as self-employed
The main restriction when working with the self–employed is the prohibition on substitution of labor relations for civil law ones. Therefore, the Law No. 422-FZ "About carrying out experiment on establishment of special tax regime "Tax on the professional income" prohibits ordering services from persons who have been employees of your company for the past two years.
If you keep lists of employees in Globas, its tools will help you to identify whether the self-employed applicant is your former employee.
Rule No. 2: check the partner's tax status
As long as the performer has the status of self-employed, he/she pays the tax on his own. However, if the status is abandoned, the customer company begins to be responsible for paying taxes and contributions.
The reasons for the loss of status may include voluntary de-registration of the self-employed, exceeding annual income of 2,4 million RUB or non-payment of tax.
It is important to understand that a change in the tax status can occur at any time: when the contract has already been signed or after the advance payment. Therefore, it is very important for customers to update this information at every stage of cooperation with a self-employed contractor.
Globas helps simplify routine tax status verification. There are two ways to check whether your potential contractor is a payer of Professional Income Tax:
- receiving information about self-employment directly when checking in the person's profile, with the ability to quickly update the status from the Federal Tax Service;
- ordering an extract "Self-employed status check" for a specific date in the "Extracts" section.
Rule No. 3: analyze the counterparty's participation in the courts of general jurisdiction, instead of arbitration ones, before concluding the contract
In case of a conflict with the self-employed, it is necessary to apply to the district courts of general jurisdiction, which implies a different approach to preparing for the case and other terms of dispute resolution than in the arbitration process.
Before entering into a contract, check whether the expert is already involved in litigation. Of course, there may be different categories of cases, and the nature of disputes may not be related to the professional qualities of the performer. But if there are many such courts, it is possible to draw unambiguous conclusions about the systemic non-fulfillment of certain obligations.
The real advantage of Globas when working with courts of general jurisdiction is the convenient search tool. Globas searches across all regions at once and offers convenient filters to narrow down search results: by type of court, case type, period and other parameters.
Rule No. 4: check for arrears, fines, penalties
Personal problems of the self-employed can affect the fulfillment of obligations. If a person does not fulfill the terms of the loan agreement, there is a court decision on debt collection and enforcement documents are transferred to bailiffs, the funds that the customer will pay for the work may be seized. That means, all the income of the self-employed will be used to repay the debt to the bank. As a result, the self-employed will not be able to purchase materials for the execution of the order, and you risk not getting the expected result of the work.
Timely check and identification of risk factors for individuals in Globas will help to learn about some problems in advance:
- overdue charges;
- judicial and extrajudicial bankruptcy;
- tax and legal debts, fines, penalties;
- active and archived enforcement proceedings.
Rule No. 5: enter into a contract
You can negotiate with the self-employed verbally, but only if you buy the finished product at sight. If your interaction with an expert requires his/her work, and the final result will be provided after any period of time, the conditions must be fixed in a written contract.
As a rule, several types of contracts are concluded with the self-employed:
- contract agreement;
- contract for the provision of paid services;
- the contract of the uniquely designed order.
Important! To avoid disputes with tax authorities, cooperate with the self-employed when it is necessary to perform specific work that is not included in the functionality of your employees. If you need an expert to perform duties for a long time, as well as if control of the work process itself is necessary, enter into an employment contract.
| You can check your counterparties of any legal form, as well as all persons associated with them for possible risks in the Information and Analytical System Globas. All information for a comprehensive check of legal entities and individuals is available in the profile of the company, individual entrepreneur and person. If you are not yet a Globas subscriber, apply for trial access, and check if there are any unreliable persons among your counterparties with whom it is better to reconsider the terms of cooperation. APPLICATION FOR TRIAL ACCESS |